Structure of human cytomegalovirus virion reveals host tRNA binding to capsid-associated tegument protein pp150
- PMID: 34535641
- PMCID: PMC8448752
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25791-1
Structure of human cytomegalovirus virion reveals host tRNA binding to capsid-associated tegument protein pp150
Abstract
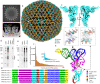
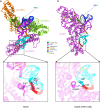
Under the Baltimore nucleic acid-based virus classification scheme, the herpesvirus human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a Class I virus, meaning that it contains a double-stranded DNA genome-and no RNA. Here, we report sub-particle cryoEM reconstructions of HCMV virions at 2.9 Å resolution revealing structures resembling non-coding transfer RNAs (tRNAs) associated with the virion's capsid-bound tegument protein, pp150. Through deep sequencing, we show that these RNA sequences match human tRNAs, and we built atomic models using the most abundant tRNA species. Based on our models, tRNA recruitment is mediated by the electrostatic interactions between tRNA phosphate groups and the helix-loop-helix motif of HCMV pp150. The specificity of these interactions may explain the absence of such tRNA densities in murine cytomegalovirus and other human herpesviruses.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

