Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development
- PMID: 34535791
- PMCID: PMC8447893
- DOI: 10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8
Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development
Abstract
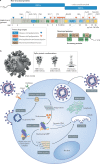
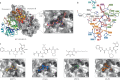
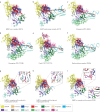
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an unprecedented global health crisis. However, therapeutic options for treatment are still very limited. The development of drugs that target vital proteins in the viral life cycle is a feasible approach for treating COVID-19. Belonging to the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae with the largest RNA genome, SARS-CoV-2 encodes a total of 29 proteins. These non-structural, structural and accessory proteins participate in entry into host cells, genome replication and transcription, and viral assembly and release. SARS-CoV-2 proteins can individually perform essential physiological roles, be components of the viral replication machinery or interact with numerous host cellular factors. In this Review, we delineate the structural features of SARS-CoV-2 from the whole viral particle to the individual viral proteins and discuss their functions as well as their potential as targets for therapeutic interventions.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

