Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development
- PMID: 34535791
- PMCID: PMC8447893
- DOI: 10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8
Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development
Abstract
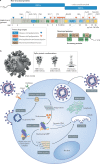
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an unprecedented global health crisis. However, therapeutic options for treatment are still very limited. The development of drugs that target vital proteins in the viral life cycle is a feasible approach for treating COVID-19. Belonging to the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae with the largest RNA genome, SARS-CoV-2 encodes a total of 29 proteins. These non-structural, structural and accessory proteins participate in entry into host cells, genome replication and transcription, and viral assembly and release. SARS-CoV-2 proteins can individually perform essential physiological roles, be components of the viral replication machinery or interact with numerous host cellular factors. In this Review, we delineate the structural features of SARS-CoV-2 from the whole viral particle to the individual viral proteins and discuss their functions as well as their potential as targets for therapeutic interventions.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2: open the door for novel therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jan 27;7(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00884-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35087058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into SARS-CoV-2 proteins.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jan 22;433(2):166725. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.11.024. Epub 2020 Nov 24. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33245961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded proteins.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Feb;65(2):280-294. doi: 10.1007/s11427-021-1964-4. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 34387838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Structural and Non-Structural Proteins and Therapeutic Targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19.Cells. 2021 Apr 6;10(4):821. doi: 10.3390/cells10040821. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33917481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Proteins: Are They Useful as Targets for COVID-19 Drugs and Vaccines?Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(1):50-66. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666210223143243. Curr Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 33622224 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of potent compounds against SARs-CoV-2: An in-silico based drug searching against Mpro.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Dec;151(Pt A):106284. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106284. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36370580 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Antiviral Drug Development: Comprehensive Insights into Design Strategies and Mechanisms Targeting Key Viral Proteins.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 28;34(7):1376-1384. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2403.03008. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38934770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic Analysis of B- and T-cell Epitopes from SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins and their Potential Cross-reactivity with Emerging Variants and other Human Coronaviruses.Arch Med Res. 2022 Nov;53(7):694-710. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.10.007. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Arch Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36336501 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 cooperates with initiation factors EIF1 and 1A to selectively enhance translation of viral RNA.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Feb 9;20(2):e1011535. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011535. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38335237 Free PMC article.
-
Tertiary folds of the SL5 RNA from the 5' proximal region of SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2320493121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2320493121. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38427602 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

