Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial
- PMID: 34536349
- PMCID: PMC8443232
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00462-X
Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial
Abstract
Background: Although SARS-CoV-2 infection often causes milder symptoms in children and adolescents, young people might still play a key part in SARS-CoV-2 transmission. An efficacious vaccine for children and adolescents could therefore assist pandemic control. For further evaluation of the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine candidate BBIBP-CorV, we assessed the safety and immunogenicity of BBIBP-CorV in participants aged 3-17 years.
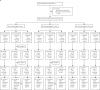
Methods: A randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial was done at Shangqiu City Liangyuan District Center for Disease Control and Prevention in Henan, China. In phases 1 and 2, healthy participants were stratified according to age (3-5 years, 6-12 years, or 13-17 years) and dose group. Individuals with a history of SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV infection were excluded. All participants were randomly assigned, using stratified block randomisation (block size eight), to receive three doses of 2 μg, 4 μg, or 8 μg of vaccine or control (1:1:1:1) 28 days apart. The primary outcome, safety, was analysed in the safety set, which consisted of participants who had received at least one vaccination after being randomly assigned, and had any safety evaluation information. The secondary outcomes were geometric meant titre (GMT) of the neutralising antibody against infectious SARS-CoV-2 and were analysed based on the full analysis set. This study is registered with www.chictr.org.cn, ChiCTR2000032459, and is ongoing.
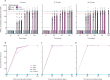
Findings: Between Aug 14, 2020, and Sept 24, 2020, 445 participants were screened, and 288 eligible participants were randomly assigned to vaccine (n=216, 24 for each dose level [2/4/8 μg] in each of three age cohorts [3-5, 6-12, and 13-17 years]) or control (n=72, 24 for each age cohort [3-5, 6-12, and 13-17 years]) in phase 1. In phase 2, 810 participants were screened and 720 eligible participants were randomly assigned and allocated to vaccine (n=540, 60 for each dose level [2/4/8 μg] in each of three age cohorts [3-5, 6-12, and 13-17 years]) or control (n=180, 60 for each age cohort [3-5, 6-12, and 13-17 years]). The most common injection site adverse reaction was pain (ten [4%] 251 participants in all vaccination groups of the 3-5 years cohort; 23 [9·1%] of 252 participants in all vaccination groups and one [1·2%] of 84 in the control group of the 6-12 years cohort; 20 [7·9%] of 252 participants in all vaccination groups of the 13-17 years cohort). The most common systematic adverse reaction was fever (32 [12·7%] of 251 participants in all vaccination groups and six [7·1%] of 84 participants in the control group of the 3-5 years cohort; 13 [5·2%] of 252 participants in the vaccination groups and one [1·2%] of 84 in the control group of the 6-12 years cohort; 26 [10·3%] of 252 participants in all vaccination groups and eight [9·5%] of 84 in the control group of the 13-17 years cohort). Adverse reactions were mostly mild to moderate in severity. The neutralising antibody GMT against the SARS-CoV-2 virus ranged from 105·3 to 180·2 in the 3-5 years cohort, 84·1 to 168·6 in the 6-12 years cohort, and 88·0 to 155·7 in the 13-17 years cohort on day 28 after the second vaccination; and ranged from 143·5 to 224·4 in the 3-5 years cohort, 127 to 184·8 in the 6-12 years cohort, and 150·7 to 199 in the 13-17 years cohort on day 28 after the third vaccination.
Interpretation: The inactivated COVID-19 vaccine BBIBP-CorV is safe and well tolerated at all tested dose levels in participants aged 3-17 years. BBIBP-CorV also elicited robust humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 infection after two doses. Our findings support the use of a 4 μg dose and two-shot regimen BBIBP-CorV in phase 3 trials in the population younger than 18 years to further ascertain its safety and protection efficacy against COVID-19.
Funding: National Program on Key Research Project of China, National Mega projects of China for Major Infectious Diseases, National Mega Projects of China for New Drug Creation, and Beijing Science and Technology Plan.
Translation: For the Chinese translation of the abstract see Supplementary Materials section.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests XMY, YTZ, YKY, HW, WW, NL, XJZ, LD, YXZ, JZ, MM, YLQ, SHZ, JJC, QQL, HF, YX, and XTZ are employees of Beijing Institute of Biological Products, which developed the vaccine and funded the trial. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

