A possible pathogenic correlation between neutrophil elastase (NE) enzyme and inflammation in the pathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 34536744
- PMCID: PMC8437823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108137
A possible pathogenic correlation between neutrophil elastase (NE) enzyme and inflammation in the pathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
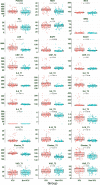
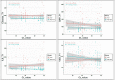
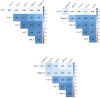
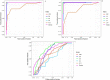
A growing body of evidence indicates that neutrophil elastase (NE) is involved in the pathogenesis of respiratory infectious diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This study aimed to analyze the dynamic changes in serum levels of NE associated with inflammation, disease activity, and mortality rate in patients with COVID-19. We measured the serum concentrations of NE, C-Reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)- 4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and vitamin D levels in 83 ICU and 69 non-ICU patients compared with 82 healthy subjects (HS) in three-time points (T1-T3). Serum levels of NE, IL-6, IL-8, and CRP in ICU and non-ICU patients were significantly higher than HS (P < 0.001) in three-time points. Also, serum levels of NE, IL-6, IL-8, and CRP in ICU patients were significantly higher than in non-ICU patients (P < 0.05). On the day of admission (T1), the levels of NE, CRP, IL-6, IL-8 were gradually decreased from T1 to T3. At the same time, IL-4 and IL-10 were gradually increased from T1 to T2 and then reduced to T3. Further analyses demonstrated that the levels of NE, IL-6, and IL-8 in deceased patients were significantly higher than in recovered patients (P < 0.05). The ROC curve analysis demonstrated that markers, including NE, IL-6, and IL-8, were valuable indicators in evaluating the activity of COVID-19. Overall, our results signify the critical role of NE in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, and also, further support that NE has a potential therapeutic target for the attenuation of COVID-19 severity.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disease activity; Inflammation; Neutrophil elastase; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Sanders J.M., Monogue M.L., Jodlowski T.Z., Cutrell J.B. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. Jama. 2020;323(18):1824–1836. - PubMed
-
- Keyvani H., Zahednasab H., Sholeh M., Mirzaei R., Esghaei M., Karampoor S. Gender Preponderance Might be Associated with the Severity of COVID-19 Infection. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2020;11:598.
-
- Mirzaei R., Mohammadzadeh R., Mahdavi F., Badrzadeh F., Kazemi S., Ebrahimi M., Soltani F., Kazemi S., Jeda A.S., Darvishmotevalli M. Overview of the current promising approaches for the development of an effective severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;106928 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

