Janus kinase (JAK)-inhibitors and coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34538216
- PMCID: PMC8500309
- DOI: 10.1080/14787210.2021.1982695
Janus kinase (JAK)-inhibitors and coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Currently, JAK-inhibitors are repurposed for therapy of Covid-19 because of their ability in restraining immune response, yet the corroboration regarding their advantage is still unclear. This study sought to analyze the efficacy of JAK-inhibitors to ameliorate the outcomes of Covid-19 sufferer.Research design and methods: Using specific keywords, we comprehensively go through the potential articles on ClinicalTrials.gov, Europe PMC, and PubMed sources until June 2nd, 2021. All published studies on JAK-inhibitors and Covid-19 were collected.
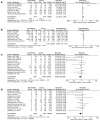
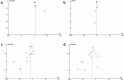
Results: There were 14 studies with 4,363 Covid-19 patients contained in the meta-analysis. Based on our data, we suggested that JAK-inhibitors corresponded with increased recovery rate (RR 1.17; 95%CI: 1.01-1.36, p= 0.040, I2 = 91%, random-effect modeling); shortened time to recovery (mean difference -0.96; 95%CI: -1.15, -0.77, p< 0.00001, I2 = 28%, random-effect modeling); reduction of clinical deterioration risk (RR 0.66; 95%CI: 0.48-0.89, p= 0.008, I2 = 57%, random-effect modeling); and reduction of Covid-19 mortality (RR 0.52; 95%CI: 0.36-0.76, p= 0.0006, I2 = 33%, random-effect modeling).
Conclusions: This study propose that JAK-inhibitors perhaps provide advantageous effects on Covid-19 outcomes. JAK-inhibitors may be given during 1-2 weeks of disease to optimize its beneficial effects in halting the exaggerated immune response.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Covid-19; JAK-inhibitors; baricitinib; treatment.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): situation report. Accessed 2021 Jun 6. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...
-
- Putri C, Hariyanto TI, Hananto JE, et al. Parkinson’s disease may worsen outcomes from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in hospitalized patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021. Apr 24;S1353-8020(21)00152–8. DOI:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2021.04.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
