Applications of nanomaterials in COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 34539132
- PMCID: PMC8442651
- DOI: 10.1007/s12598-021-01789-y
Applications of nanomaterials in COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
The novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic represents one of the biggest global health threats in the last two decades, so researchers around the world are searching for solutions and treatments for COVID-19. At the time of writing, there are no specific drugs that have demonstrated suitable effectiveness in treating COVID-19. The current challenge involves designing tools for the prevention, rapid and accurate diagnosis, drug delivery, and effective treatment of this novel coronavirus. In this short review, we discuss how nanotechnology offers new ways to combat COVID-19, and how nanomaterials can be applied to control the COVID-19 outbreak. We also summarize relevant studies regarding the use of nanomaterials for preventing viral spread, preparing vaccines, and diagnosing coronavirus, as well as studies that show how nanoparticles can be used as drug delivery systems for the treatment of viral infections. Research on nanotechnology-based diagnosis, drug delivery, and antiviral therapy is currently in the early stages. However, the unique chemical properties of some nanomaterials highlight the broad prospect of nanomaterials in the future, and we propose that they will play an important role in the fight against COVID-19.
新型冠状病毒-2019(COVID-19)大流行是过去20年最大的全球健康威胁之一, 因此世界各地的研究人员正在寻找COVID-19的解决方案和治疗方法。截至到撰写本文的时候, 研究人员发现还没有有效治疗COVID-19的特定药物。现阶段研究人员所面临的主要挑战是设计预防这种新型冠状病毒、快速准确诊断、药物传递和有效治疗的纳米工具。我们在这篇简短的综述中讨论了纳米技术如何为抗击COVID-19提供新方法, 还讨论了纳米材料如何应用于控制COVID-19爆发。同时, 我们还总结了纳米材料在预防COVID-19病毒传播、制备疫苗、诊断冠状病毒等方面的相关研究, 以及纳米材料作为药物递送系统治疗该病毒感染的研究。现阶段, 基于纳米技术的诊断、药物传递和抗病毒治疗的研究还处于早期阶段。然而, 一些纳米材料独特的化学性质凸显了纳米材料在未来的广阔前景, 我们认为它们将在抗击COVID-19中发挥十分重要的作用。.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronaviruses; Nanomaterials; Viral control.
© Youke Publishing Co.,Ltd 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
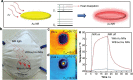

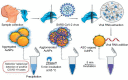
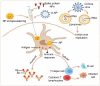
References
-
- Adhikari S, Adhikari U, Mishra A, Guragain B. Nanomaterials for diagnostic, treatment and prevention of COVID-19. Appl Sci Technol Annals. 2020;1:155. doi: 10.3126/asta.v1i1.30295. - DOI
-
- Liu T, Hu J, Kang M, Lin L, Zhong H, Xiao J. Transmission dynamics of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). SSRN Electron J. 2020. 10.2139/ssrn.3526307.
-
- Sankar S V., Mohanan Pillai A., Rahdar A., Anumol P., Phd N., Mitropoulos A., Mokarrar M., Kyzas G. On Facing the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) with Combination of Nanomaterials and Medicine: Possible Strategies and First Challenges. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(5):852. doi: 10.3390/nano10050852. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
