Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hepatotoxicity: A review
- PMID: 34539139
- PMCID: PMC8409159
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i32.5376
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hepatotoxicity: A review
Abstract
The application of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in advanced cancer has been a major development in the last decade. The indications for ICIs are constantly expanding into new territory across different cancers, disease stages and lines of therapy. With this increased use, adverse events including immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hepatotoxicity (ICH) have emerged as an important clinical problem. This along with the introduction of ICI as first- and second-line treatments for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma makes ICH very relevant to gastroenterologists and hepatologists. The incidence of ICH varies between 1%-20% depending on the number, type and dose of ICI received. Investigation and management generally involve excluding differential diagnoses and following a stepwise escalation of withholding or ceasing ICI, corticosteroid treatment and adding other immunosuppressive agents depending on the severity of toxicity. The majority of patients with ICH recover and some may even safely recommence ICI therapy. Guideline recommendations are largely based on evidence derived from retrospective case series which highlights a priority for future research.
Keywords: Adverse drug event; Drug-induced liver injury; Hepatitis; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immunosuppression; Immunotherapy.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
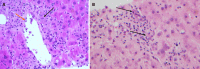
Figures
References
-
- Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W, van den Eertwegh AJ, Lutzky J, Lorigan P, Vaubel JM, Linette GP, Hogg D, Ottensmeier CH, Lebbé C, Peschel C, Quirt I, Clark JI, Wolchok JD, Weber JS, Tian J, Yellin MJ, Nichol GM, Hoos A, Urba WJ. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–723. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO, Li D, Verret W, Xu DZ, Hernandez S, Liu J, Huang C, Mulla S, Wang Y, Lim HY, Zhu AX, Cheng AL IMbrave150 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1894–1905. - PubMed
-
- El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, Kim TY, Choo SP, Trojan J, Welling TH Rd, Meyer T, Kang YK, Yeo W, Chopra A, Anderson J, Dela Cruz C, Lang L, Neely J, Tang H, Dastani HB, Melero I. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2492–2502. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Ryoo BY, Merle P, Kudo M, Bouattour M, Lim HY, Breder V, Edeline J, Chao Y, Ogasawara S, Yau T, Garrido M, Chan SL, Knox J, Daniele B, Ebbinghaus SW, Chen E, Siegel AB, Zhu AX, Cheng AL KEYNOTE-240 investigators. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:193–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

