Complication and Sequelae of COVID-19: What Should We Pay Attention to in the Post-Epidemic Era
- PMID: 34539642
- PMCID: PMC8446426
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711741
Complication and Sequelae of COVID-19: What Should We Pay Attention to in the Post-Epidemic Era
Abstract
COVID-19 is widespread worldwide and seriously affects the daily life and health of humans. Countries around the world are taking necessary measures to curb the spread. However, COVID-19 patients often have at least one organ complication and sequelae in addition to respiratory symptoms. Controlling the epidemic is only a phased victory, and the complication and sequelae of COVID-19 will need more attention in the post-epidemic era. We collected general information from over 1000 articles published in 2020 after the COVID-19 outbreak and systematically analyzed the complication and sequelae associated with eight major systems in COVID-19 patients caused by ACE2 intervention in the RAS regulatory axis. The autoimmune response induced by 2019-nCoV attacks and damages the normal tissues and organs of the body. Our research will help medical workers worldwide address COVID-19 complication and sequelae.
Keywords: COVID-19; Web of Science; bibliometric analysis; complication; eight systems; sequelae.
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Wen, Wang, Zhou, Da, Meng, Xue and Tao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
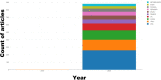
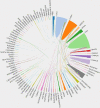
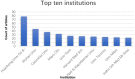
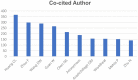

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

