Wood Anatomy of Douglas-Fir in Eastern Arizona and Its Relationship With Pacific Basin Climate
- PMID: 34539695
- PMCID: PMC8440974
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.702442
Wood Anatomy of Douglas-Fir in Eastern Arizona and Its Relationship With Pacific Basin Climate
Abstract
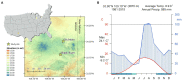
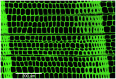
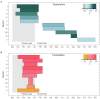
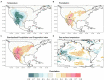
Dendroclimatic reconstructions, which are a well-known tool for extending records of climatic variability, have recently been expanded by using wood anatomical parameters. However, the relationships between wood cellular structures and large-scale climatic patterns, such as El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), are still not completely understood, hindering the potential for wood anatomy as a paleoclimatic proxy. To better understand the teleconnection between regional and local climate processes in the western United States, our main objective was to assess the value of these emerging tree-ring parameters for reconstructing climate dynamics. Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy, we measured cell lumen diameter and cell wall thickness (CWT) for the period 1966 to 2015 in five Douglas-firs [Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco] from two sites in eastern Arizona (United States). Dendroclimatic analysis was performed using chronologies developed for 10 equally distributed sectors of the ring and daily climatic records to identify the strongest climatic signal for each sector. We found that lumen diameter in the first ring sector was sensitive to previous fall-winter temperature (September 25th to January 23rd), while a precipitation signal (October 27th to February 13th) persisted for the entire first half of the ring. The lack of synchronous patterns between trees for CWT prevented conducting meaningful climate-response analysis for that anatomical parameter. Time series of lumen diameter showed an anti-phase relationship with the Southern Oscillation Index (a proxy for ENSO) at 10 to 14year periodicity and particularly in 1980-2005, suggesting that chronologies of wood anatomical parameters respond to multidecadal variability of regional climatic modes. Our findings demonstrate the potential of cell structural characteristics of southwestern United States conifers for reconstructing past climatic variability, while also improving our understanding of how large-scale ocean-atmosphere interactions impact local hydroclimatic patterns.
Keywords: El Niño/Southern Oscillation; Pacific Decadal Oscillation; Pseudotsuga menziesii; paleoclimate; quantitative wood anatomy; western United States.
Copyright © 2021 Balanzategui, Nordhauß, Heinrich, Biondi, Miley, Hurley and Ziaco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arzac A., Babushkina E. A., Fonti P., Slobodchikova V., Sviderskaya I. V., Vaganov E. A. (2018). Evidences of wider latewood in Pinus sylvestris from a forest-steppe of southern Siberia. Dendrochronologia 49, 1–8. 10.1016/j.dendro.2018.02.007 - DOI
-
- Beck W., Sanders T. G. M., Pofahl U. (2013). CLIMTREG: detecting temporal changes in climate-growth reactions - a computer program using intra-annual daily and yearly moving time intervals of variable width. Dendrochronologia 31, 232–241. 10.1016/j.dendro.2013.02.003 - DOI
-
- Beguería S., Vicente-Serrano S. M., Reig F., Latorre B. (2014). Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) revisited: parameter fitting, evapotranspiration models, tools, datasets and drought monitoring. Int. J. Climatol. 34, 3001–3023. 10.1002/joc.3887 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

