Immune suppression reversal of the spleen: a promising strategy for improving the survival rate of sepsis in rats
- PMID: 34540012
- PMCID: PMC8430070
Immune suppression reversal of the spleen: a promising strategy for improving the survival rate of sepsis in rats
Abstract
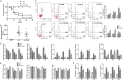
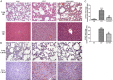
Evidence suggests that immune dysfunction exerts a central role in the morbidity and mortality of sepsis. As the spleen is the largest lymphatic tissue in the body, its influence on immune regulation during sepsis should be explored. In this study, we analysed the immune alterations of the spleen of septic rats and the effects of splenectomy at 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h following caecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Results showed declines in CD4+ T cells and elevations in lymphocyte apoptosis, the percentage of Treg cells, and inflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10) in the spleens of CLP-induced septic rats. Moreover, splenectomy improved the survival of septic rats and bacterial clearance from peripheral blood. CLP-induced apoptosis of lymphocytes and the decreased CD4+ T cell percentage in the peripheral blood could be reversed in splenectomy-treated rats. Splenectomy greatly decreased the number of white blood cells, lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, and serum concentration of TNF-α and IL-10 after CLP. Moreover, splenectomy alleviated pathologic damage to the liver and lungs and weakened expression of CD163. These novel findings demonstrate that immune disorders of the spleen are important pathogenic factors during the course of severe sepsis. Splenectomy could alleviate apoptosis and reduction of lymphocytes induced by sepsis, and lower the level of inflammation in the body. Reversing the immune suppression of the spleen may be a novel strategy to improve sepsis survival.
Keywords: CD163; Splenectomy; cell apoptosis; immune suppression; sepsis.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Splenectomy provides protective effects against CLP-induced sepsis by reducing TRegs and PD-1/PD-L1 expression.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021 Jul;136:105970. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.105970. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33774183
-
Tanshinone IIA attenuates sepsis-induced immunosuppression and improves survival rate in a mice peritonitis model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108609. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108609. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30784917
-
Baicalein Attenuates Severe Polymicrobial Sepsis via Alleviating Immune Dysfunction of T Lymphocytes and Inflammation.Chin J Integr Med. 2022 Aug;28(8):711-718. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3510-7. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Chin J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 35355199
-
[Reproduction of a model of "two-hit" sepsis model with complication of pneumonia in rat].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Oct;27(10):805-10. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 27132442 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic effect of human ghrelin and growth hormone: Attenuation of immunosuppression in septic aged rats.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Oct;1863(10 Pt B):2584-2593. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28115288 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Splenectomy for treating hepatosplenic candidiasis: Two cases and literature review suggesting its feasibility.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 3;9(4):e15114. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15114. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37089309 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
