The effect of individual nursing on improving the living ability and blood sugar control of Alzheimer disease patients with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 34540049
- PMCID: PMC8430077
The effect of individual nursing on improving the living ability and blood sugar control of Alzheimer disease patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of individual nursing on Alzheimer disease (AD) patients with diabetes mellitus.
Methods: A total of 119 patients with AD complicated with diabetes admitted to our hospital from January 2017 to January 2019 were selected for prospective analysis, and 64 patients received individual nursing mode, which were regarded as the personality group (PG). Another 55 patients received routine nursing mode and were regarded as the regular group (RG). The curative effect of AD, blood glucose, living ability, cognitive function, self-care ability and nursing satisfaction of the two groups were investigated.
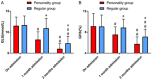
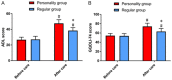
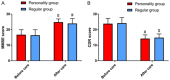
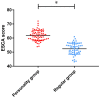
Results: There was no difference between the two groups in AD curative effect and cognitive function (P > 0.05), and the blood sugar control, living ability, self-care ability and nursing satisfaction of the PG were higher than those of the RG (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Individual nursing can effectively improve the ability of blood sugar control and daily life of AD patients with diabetes mellitus, and greatly enhance the patients' trust, dependence, and satisfaction with medical staff, which is worth popularizing in clinical practice.
Keywords: AD; Individual nursing; blood sugar; diabetes; living ability.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Niu H, Alvarez-Alvarez I, Guillen-Grima F, Aguinaga-Ontoso I. Prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer’s disease in Europe: a meta-analysis. Neurologia. 2017;32:523–532. - PubMed
-
- Desikan RS, Fan CC, Wang Y, Schork AJ, Cabral HJ, Cupples LA, Thompson WK, Besser L, Kukull WA, Holland D, Chen CH, Brewer JB, Karow DS, Kauppi K, Witoelar A, Karch CM, Bonham LW, Yokoyama JS, Rosen HJ, Miller BL, Dillon WP, Wilson DM, Hess CP, Pericak-Vance M, Haines JL, Farrer LA, Mayeux R, Hardy J, Goate AM, Hyman BT, Schellenberg GD, McEvoy LK, Andreassen OA, Dale AM. Genetic assessment of age-associated Alzheimer disease risk: development and validation of a polygenic hazard score. PLoS Med. 2017;14:e1002258. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schumann C, Alexopoulos P, Perneczky R. Determinants of self- and carer-rated quality of life and caregiver burden in Alzheimer disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019;34:1378–1385. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
