Acute anterior uveitis after topical interferon for conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)
- PMID: 34540523
- PMCID: PMC8422938
- DOI: 10.3205/oc000184
Acute anterior uveitis after topical interferon for conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)
Abstract
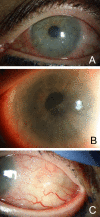
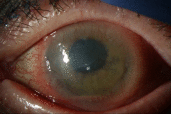
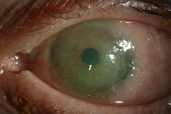
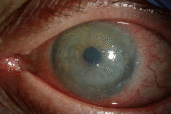
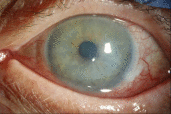
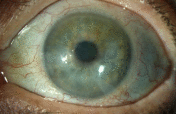
Objective: Ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) is the most common type of non-melanocytic ocular surface tumor. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a type of OSSN that be medically managed by either topical interferon alpha-2b (IFN α-2b), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), or mitomycin C. While a paradoxical response to IFN α-2b in the HIV population has been reported, we report a case of a paradoxical response in an immunocompetent individual. Methods: A 65-year-old immunocompetent female presents to the clinic with CIN. Results: She is started on topical IFN α-2b, resulting in an unexpected hypopyon, increased corneal epithelial defect, and increased size of the lesion. Switching to topical 5-FU resulted in decreasing size of the CIN lesion and resolution of the epithelial defect. Conclusions: Topical IFN α-2b can produce a paradoxical worsening of CIN lesions in some patients. Providers should be aware of this reaction, as well as the presenting signs and symptoms, to make appropriate treatment changes when treating CIN.
Keywords: 5-FU; CIN; IFN alpha-2b; OSSN; anterior uveitis.
Copyright © 2021 Naravane et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mata E, Conesa E, Castro M, Martínez L, de Pablo C, González ML. Carcinoma epidermoide conjuntival: respuesta paradójica al colirio interferón. [Conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma: paradoxical response to interferon eyedrops]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2014 Jul;89(7):293–296. doi: 10.1016/j.oftal.2012.12.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

