Algorithm combining virtual chromoendoscopy features for colorectal polyp classification
- PMID: 34540541
- PMCID: PMC8445691
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1512-5175
Algorithm combining virtual chromoendoscopy features for colorectal polyp classification
Abstract
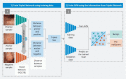
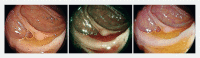
Background and study aims Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard for decreasing colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps (CRPs) is an ongoing challenge in clinical colonoscopy and its accuracy among endoscopists varies widely. Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for CRP characterization may help to improve this accuracy. In this study, we investigated the diagnostic accuracy of a novel algorithm for polyp malignancy classification by exploiting the complementary information revealed by three specific modalities. Methods We developed a CAD algorithm for CRP characterization based on high-definition, non-magnified white light (HDWL), Blue light imaging (BLI) and linked color imaging (LCI) still images from routine exams. All CRPs were collected prospectively and classified into benign or premalignant using histopathology as gold standard. Images and data were used to train the CAD algorithm using triplet network architecture. Our training dataset was validated using a threefold cross validation. Results In total 609 colonoscopy images of 203 CRPs of 154 consecutive patients were collected. A total of 174 CRPs were found to be premalignant and 29 were benign. Combining the triplet network features with all three image enhancement modalities resulted in an accuracy of 90.6 %, 89.7 % sensitivity, 96.6 % specificity, a positive predictive value of 99.4 %, and a negative predictive value of 60.9 % for CRP malignancy classification. The classification time for our CAD algorithm was approximately 90 ms per image. Conclusions Our novel approach and algorithm for CRP classification differentiates accurately between benign and premalignant polyps in non-magnified endoscopic images. This is the first algorithm combining three optical modalities (HDWL/BLI/LCI) exploiting the triplet network approach.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests This study was financially supported by the Catharina Research Foundation.
Figures
References
-
- Torre L A, Bray F, Siegel R L et al.Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Rex D K, Kahi C, OʼBrien M et al.The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI (Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations) on real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:419–422. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

