Therapeutic Effects of an Inhibitor of Thioredoxin Reductase on Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β1/Smads Pathway
- PMID: 34540892
- PMCID: PMC8440796
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.690170
Therapeutic Effects of an Inhibitor of Thioredoxin Reductase on Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β1/Smads Pathway
Abstract
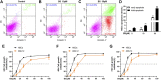
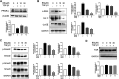
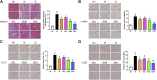
Liver fibrosis is an important stage in the progression of liver injury into cirrhosis or even liver cancer. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are induced by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) to produce α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagens in liver fibrosis. Butaselen (BS), which was previously synthesized by our group, is an organic selenium compound that exerts antioxidant and tumor cell apoptosis-promoting effects by inhibiting the thioredoxin (Trx)/thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) system. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential effects of BS on liver fibrosis and explore the underlying molecular mechanisms of its action. Liver fibrosis models were established using male BALB/c mice through intraperitoneal injection of CCl4. BS was administered orally once daily at a dose of 36, 90, or 180 mg/kg. Silymarin (Si), which is a drug used for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, was administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg per day as a control. The action mechanisms of BS against liver fibrosis progression were examined in HSCs. The study revealed that the activity and expression levels of TrxR were elevated in the mouse liver and serum after CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Oral administration of BS relieved the pathological state of mice with liver fibrosis, showing significant therapeutic effects against liver fibrosis. Moreover, BS not only induced HSC apoptosis but also inhibited the production of α-SMA and collagens by HSCs by downregulating the TGF-β1 expression and blocking the TGF-β1/Smads pathway. The results of the study indicated that BS inhibited liver fibrosis by regulating the TGF-β1/Smads pathway.
Keywords: collagen; hepatic stellate cells; liver fibrosis; thioredoxin reductase; transforming growth factor-β1; α-SMA.
Copyright © 2021 Jiao, Bai, Yin, Liu, Sun, Su, Zeng and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
Author HY was employed by the company Shanghai Yuanxi Medicine Corp. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Blaner W. S., O'Byrne S. M., Wongsiriroj N., Kluwe J., D'Ambrosio D. M., Jiang H., et al. (2009). Hepatic Stellate Cell Lipid Droplets: a Specialized Lipid Droplet for Retinoid Storage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Bba) - Mol. Cel Biol. Lipids 1791 (6), 467–473. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.11.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chasapis C. T., Makridakis M., Damdimopoulos A. E., Zoidakis J., Lygirou V., Mavroidis M., et al. (2019). Implications of the Mitochondrial Interactome of Mammalian Thioredoxin 2 for normal Cellular Function and Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 137, 59–73. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.018 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

