The Functions of BET Proteins in Gene Transcription of Biology and Diseases
- PMID: 34540900
- PMCID: PMC8446420
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.728777
The Functions of BET Proteins in Gene Transcription of Biology and Diseases
Abstract
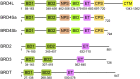
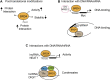
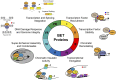
The BET (bromodomain and extra-terminal domain) family proteins, consisting of BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, and testis-specific BRDT, are widely acknowledged as major transcriptional regulators in biology. They are characterized by two tandem bromodomains (BDs) that bind to lysine-acetylated histones and transcription factors, recruit transcription factors and coactivators to target gene sites, and activate RNA polymerase II machinery for transcriptional elongation. Pharmacological inhibition of BET proteins with BD inhibitors has been shown as a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of many human diseases including cancer and inflammatory disorders. The recent advances in bromodomain protein biology have further uncovered the complex and versatile functions of BET proteins in the regulation of gene expression in chromatin. In this review article, we highlight our current understanding of BET proteins' functions in mediating protein-protein interactions required for chromatin-templated gene transcription and splicing, chromatin remodeling, DNA replication, and DNA damage repair. We further discuss context-dependent activator vs. repressor functions of individual BET proteins, isoforms, and bromodomains that may be harnessed for future development of BET bromodomain inhibitors as emerging epigenetic therapies for cancer and inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: bromodomain; bromodomain and extra-terminal domain proteins; cancer; gene transcription; inhibitors.
Copyright © 2021 Cheung, Kim and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
M-MZ is a founder, director, and shareholder of Parkside Scientific, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
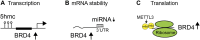
Similar articles
-
The Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Family: Functional Anatomy of BET Paralogous Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 7;17(11):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111849. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27827996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective inhibition of the BD2 bromodomain of BET proteins in prostate cancer.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7794):306-310. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1930-8. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31969702
-
Epigenetic Readers of Lysine Acetylation Regulate Cocaine-Induced Plasticity.J Neurosci. 2015 Nov 11;35(45):15062-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0826-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26558777 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of estrogen receptor function to BET bromodomain inhibition is mediated by transcriptional coactivator cooperativity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 26:2024.07.25.605008. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.25.605008. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Jan;32(1):98-112. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01384-6. PMID: 39211208 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
BET Bromodomain Inhibitors: Novel Design Strategies and Therapeutic Applications.Molecules. 2023 Mar 29;28(7):3043. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073043. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Identification, Evolution, and Expression Analysis of Bromodomain Genes Family in Buffalo.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 1;13(1):103. doi: 10.3390/genes13010103. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052443 Free PMC article.
-
A new vulnerability to BET inhibition due to enhanced autophagy in BRCA2 deficient pancreatic cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Sep 21;14(9):620. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06145-9. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37735513 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Tumors of the Nervous System: New Insights into Signaling, Genetics and Therapeutic Targeting".Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8700. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158700. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955830 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Modeling of Protein-Polypeptide Complexes by Bayesian Model Selection using AlphaFold and NMR Chemical Shift Perturbation Data.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 22:2024.09.19.613999. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.19.613999. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345459 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Inhibition of BRD4 Promotes Pexophagy by Increasing ROS and ATM Activation.Cells. 2022 Sep 12;11(18):2839. doi: 10.3390/cells11182839. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139416 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

