Carrier-free nanodrugs with efficient drug delivery and release for cancer therapy: From intrinsic physicochemical properties to external modification
- PMID: 34541398
- PMCID: PMC8424425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.06.035
Carrier-free nanodrugs with efficient drug delivery and release for cancer therapy: From intrinsic physicochemical properties to external modification
Abstract
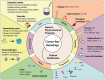
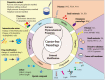
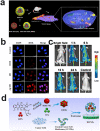
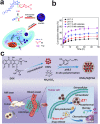
The considerable development of carrier-free nanodrugs has been achieved due to their high drug-loading capability, simple preparation method, and offering "all-in-one" functional platform features. However, the native defects of carrier-free nanodrugs limit their delivery and release behavior throughout the in vivo journey, which significantly compromise the therapeutic efficacy and hinder their further development in cancer treatment. In this review, we summarized and discussed the recent strategies to enhance drug delivery and release of carrier-free nanodrugs for improved cancer therapy, including optimizing the intrinsic physicochemical properties and external modification. Finally, the corresponding challenges that carrier-free nanodrugs faced are discussed and the future perspectives for its application are presented. We hope this review will provide constructive information for the rational design of more effective carrier-free nanodrugs to advance therapeutic treatment.
Keywords: Carrier-free nanodrugs; Drug delivery and release; External modification; Intrinsic physicochemical properties; Therapeutic efficacy.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Zhu Y., He Y., Su T., Li C., Cai S., Wu Z., Huang D., Zhang X., Cao J., He B. Exogenous vitamin c triggered structural changes of redox-activated dual core-crosslinked biodegradable nanogels for boosting the antitumor efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2020;8:5109–5116. doi: 10.1039/d0tb00356e. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

