SPI2 T3SS effectors facilitate enterocyte apical to basolateral transmigration of Salmonella-containing vacuoles in vivo
- PMID: 34542008
- PMCID: PMC8475570
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1973836
SPI2 T3SS effectors facilitate enterocyte apical to basolateral transmigration of Salmonella-containing vacuoles in vivo
Abstract
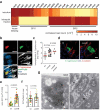
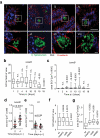
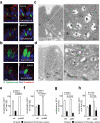
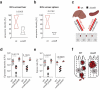
Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI) 2 type three secretion system (T3SS)-mediated effector molecules facilitate bacterial survival in phagocytes but their role in the intestinal epithelium in vivo remains ill-defined. Using our neonatal murine infection model in combination with SPI2 reporter technology and RNA-Seq of sorted primary enterocytes, we demonstrate expression of SPI2 effector molecules by intraepithelial Salmonella Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium). Contrary to expectation, immunostaining revealed that infection with SPI2 T3SS-mutants resulted in significantly enlarged intraepithelial Salmonella-containing vacuoles (SCV) with altered cellular positioning, suggesting impaired apical to basolateral transmigration. Also, infection with isogenic tagged S. Typhimurium strains revealed a reduced spread of intraepithelial SPI2 T3SS mutant S. Typhimurium to systemic body sites. These results suggest that SPI2 T3SS effector molecules contribute to enterocyte apical to basolateral transmigration of the SCV during the early stage of the infection.
Keywords: Salmonella; Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (Spi-2); apical to basolateral transmigration; enterocyte; mucosal translocation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
