Circular RNA repertoires are associated with evolutionarily young transposable elements
- PMID: 34542406
- PMCID: PMC8516420
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67991
Circular RNA repertoires are associated with evolutionarily young transposable elements
Abstract
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are found across eukaryotes and can function in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Their biogenesis through a circle-forming backsplicing reaction is facilitated by reverse-complementary repetitive sequences promoting pre-mRNA folding. Orthologous genes from which circRNAs arise, overall contain more strongly conserved splice sites and exons than other genes, yet it remains unclear to what extent this conservation reflects purifying selection acting on the circRNAs themselves. Our analyses of circRNA repertoires from five species representing three mammalian lineages (marsupials, eutherians: rodents, primates) reveal that surprisingly few circRNAs arise from orthologous exonic loci across all species. Even the circRNAs from orthologous loci are associated with young, recently active and species-specific transposable elements, rather than with common, ancient transposon integration events. These observations suggest that many circRNAs emerged convergently during evolution - as a byproduct of splicing in orthologs prone to transposon insertion. Overall, our findings argue against widespread functional circRNA conservation.
Keywords: circRNA; evolution; evolutionary biology; genetics; genomics; human; mammals; mouse; rat; rhesus macaque; splicing; transposons.
© 2021, Gruhl et al.
Conflict of interest statement
FG, PJ, HK, DG No competing interests declared
Figures





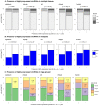

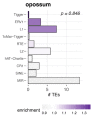



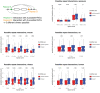
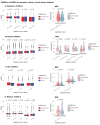
References
-
- Alhasan AA, Izuogu OG, Al-Balool HH, Steyn JS, Evans A, Colzani M, Ghevaert C, Mountford JC, Marenah L, Elliott DJ, Santibanez-Koref M, Jackson MS. Circular RNA enrichment in platelets is a signature of transcriptome degradation. Blood. 2016;127:e1–e11. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-06-649434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amit M, Donyo M, Hollander D, Goren A, Kim E, Gelfman S, Lev-Maor G, Burstein D, Schwartz S, Postolsky B, Pupko T, Ast G. Differential GC content between exons and introns establishes distinct strategies of splice-site recognition. Cell Reports. 2012;1:543–556. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.03.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bachmayr-Heyda A, Reiner AT, Auer K, Sukhbaatar N, Aust S, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Mesteri I, Grunt TW, Zeillinger R, Pils D. Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation--exemplified with colorectal and ovarian Cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Scientific Reports. 2015;5:8057. doi: 10.1038/srep08057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- SRA/SRA052697
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

