Compound 21, a Direct AT2R Agonist, Induces IL-10 and Inhibits Inflammation in Mice Following Traumatic Brain Injury
- PMID: 34542832
- PMCID: PMC9479688
- DOI: 10.1007/s12017-021-08687-7
Compound 21, a Direct AT2R Agonist, Induces IL-10 and Inhibits Inflammation in Mice Following Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
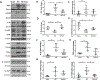
Recent studies demonstrated that the angiotensin type 2 receptor (AT2R) agonist, compound 21 (C21), provides neuroprotection and enhances recovery in experimental stroke. However, C21 has never been tested in traumatic brain injury (TBI). Here, we aim to examine whether C21 confers protection after TBI. Unilateral cortical impact injury was induced in young adult C57BL/6 mice. C21 (0.03 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered at 1 h and 3 h post-TBI. After neurological severity score (NSS) assessments, all animals were sacrificed for immunoblotting analysis at 24 h post-TBI. C21 treatment significantly ameliorated NSS and reduced TBI's biomarkers [high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), aquaporin-4 (AQ4)] and inflammatory markers [interlukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)] in the pericontusional areas compared to saline TBI. Further, C21 treatment induced interleukin-10 (IL-10) and phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) after TBI. C21 also attenuated pro-apoptotic activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and caspase-3. These findings support the therapeutic potential of C21 against TBI.
Keywords: AQ4; AT2R; Compound 21; Inflammation; TBI.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed HA, Ishrat T, Pillai B, Bunting KM, Patel A, Vazdarjanova A, et al. (2018a). Role of angiotensin system modulation on progression of cognitive impairment and brain MRI changes in aged hypertensive animals—A randomized double- blind pre-clinical study. Behavioural Brain Research, 346, 29–40. 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.12.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cuthbert JP, Harrison-Felix C, Corrigan JD, Kreider S, Bell JM, Coronado VG, et al. (2015). Epidemiology of adults receiving acute inpatient rehabilitation for a primary diagnosis of traumatic brain injury in the United States. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 30(2), 122–135. 10.1097/HTR.0000000000000012 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

