Insomnia and suicide as reported adverse effects of second-generation antipsychotics and mood stabilizers
- PMID: 34543183
- PMCID: PMC8804988
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.9646
Insomnia and suicide as reported adverse effects of second-generation antipsychotics and mood stabilizers
Abstract
Study objectives: Insomnia and suicide ideation/behavior/death (SIB) are common in psychiatric disorders. There is evidence that clozapine and lithium have antisuicidal properties and beneficial effects on sleep. We investigated the reported odds of spontaneously reported psychiatric adverse drug reactions of insomnia and SIB in adults for second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and mood stabilizers compared to clozapine and lithium, respectively.
Methods: We searched the U.S. Food & Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System from inception through February 2021 for which an SGA or mood stabilizer was the suspected agent of a psychiatric adverse drug reaction.
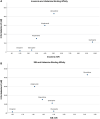
Results: We investigated 10 SGAs and 5 mood stabilizers. Compared to clozapine, other SGAs were associated with a significantly increased reported odds of insomnia (reported odds ratio [rOR] = 2.41-9.70) and SIB (rOR = 1.18-2.72). Compared to lithium, there was a significantly increased reported odds of SIB (rOR = 1.17-1.70) for other mood stabilizers and odds of insomnia (rOR = 1.66) for lamotrigine. The insomnia and SIB rORs for SGAs and mood stabilizers were positively correlated.
Conclusions: Our results are consistent with evidence for antisuicidal properties of clozapine and lithium. Findings also raise the possibility of beneficial effects on sleep as one potential pathway underlying the antisuicidal properties for these agents. Future studies are needed to identify underlying biological mechanisms that contribute to these associations.
Citation: Miller BJ, McCall WV. Insomnia and suicide as reported adverse effects of second-generation antipsychotics and mood stabilizers. J Clin Sleep Med. 2022;18(2):517-522.
Keywords: adverse drug reaction; antipsychotics; clozapine; insomnia; lithium; mood stabilizers; suicide.
© 2022 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have seen and approved the manuscript. Work for this study was performed at Augusta University. Dr. Miller has nothing to disclose for the work under consideration. In the past 12 months, Dr. Miller received research support from Augusta University, the National Institute of Mental Health, and the Stanley Medical Research Institute; participated in advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim; and received honoraria from Atheneum, Clearview Healthcare Partners, and
Figures

Comment in
-
You lack the season of all natures, sleep.J Clin Sleep Med. 2022 Feb 1;18(2):343-344. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.9826. J Clin Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 34857085 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Meltzer HY , Alphs L , Green AI , et al. .; International Suicide Prevention Trial Study Group . Clozapine treatment for suicidality in schizophrenia: International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT) . Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003. ; 60 ( 1 ): 82 – 91 . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

