Xylanase impact beyond performance: A microbiome approach in laying hens
- PMID: 34543338
- PMCID: PMC8452031
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257681
Xylanase impact beyond performance: A microbiome approach in laying hens
Abstract
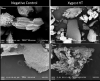
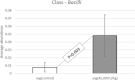
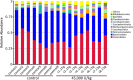
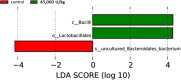
Anti-nutritional compounds such as non-starch polysaccharides (NSP) are present in viscous cereals used in feed for poultry. Therefore, exogenous carbohydrases are commonly added to monogastric feed to degrade these NSP. Our hypothesis is that xylanase not only improves laying hen performance and digestibility, but also induces a significant shift in microbial composition within the intestinal tract and thereby might exert a prebiotic effect. In this context, a better understanding on whether and how the chicken gut microbial population can be modulated by xylanase is required. To do so, the effects of dietary supplementation of xylanase on performance, apparent total tract digestibility (ATTD) and cecal microbiome in laying hens were evaluated in the present study. A total of 96 HiSex laying hens were used in this experiment (3 diets and 16 replicates of 2 hens). Xylanase was added to the diets at concentrations of 0, 45,000 (15 g/t XygestTM HT) and 90,000 U/kg (30 g/t Xygest HT). The diets were based on wheat (~55%), soybean and sunflower meal. The lowest dosage, 45,000 U/kg, significantly increased average egg weight and improved feed efficiency compared to the control treatment (P<0.05). Egg quality parameters were significantly improved in the experiment in response to the xylanase addition. For example, during the last 28 days of the trial, birds receiving the 45,000 U/kg and the 90,000 U/kg treatments exhibited an increase in Haugh units and albumin heights (P<0.05). Compared with the control, the ATTD of organic matter and crude protein were drastically improved in the 45,000 U/kg treatment group (P<0.05). Furthermore, gross energy and the ATTD of crude fat were improved significantly for birds fed 90,000 U/kg group compared to the control. Importantly, 16S rRNA gene analysis revealed that xylanase at 45,000 U/kg dosage can exert a change in the cecal microbiome. A significant increase in beneficial bacteria (Bacilli class; Enterococcaceae and Lactobacillales orders; Merdibacter, Enterococcus and Nocardiopsis genera; Enterococcus casseliflavus species) was documented when adding 45,000 U/kg xylanase to the diet of laying hens. In conclusion, dietary supplementation of xylanase 45,000 U/kg significantly improved laying hen performance and digestibility. Furthermore, microbiome data suggest that xylanase modulates the laying hen bacterial population beneficially, thus potentially exerting a prebiotic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The funding is funded by Kemin Europa N.V. This does not alter the authors’ adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures







References
-
- Hahn-Didde D, Purdum SE. The effects of an enzyme complex in moderate and low nutrient-dense diets with dried distillers grains with solubles in laying hens. Journal of Applied Poultry Research. 2014;23:23–33.
-
- Dillon GP, Filer K, Gaffney M, Moran CA. Validation of an analytical method for the determination of the activity of xylanase in animal feed additives and in animal feedingstuffs. Journal of Applied Animal Nutrition. 2015;3:1–11.
-
- Choct M. Enzymes for the feed industry: past, present and future. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2006;62:5–16.
-
- Erdaw MM, Bhuiyan MM, Iji PA. Enhancing the nutritional value of soybeans for poultry through supplementation with new-generation feed enzymes. World’s Poult. Sci. J.2016;72:307–322.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

