Reboxetine Plus Oxybutynin for OSA Treatment: A 1-Week, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Crossover Trial
- PMID: 34543665
- PMCID: PMC10835052
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.08.080
Reboxetine Plus Oxybutynin for OSA Treatment: A 1-Week, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Crossover Trial
Abstract
Background: The recent discovery that a combination of noradrenergic and antimuscarinic drugs improved upper airway muscle function during sleep and reduced OSA severity has revitalized interest in pharmacologic therapies for OSA.
Research question: Would 1 week of reboxetine plus oxybutynin (Reb-Oxy) be effective on OSA severity?
Study design and methods: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover trial was performed comparing 4 mg reboxetine plus 5 mg oxybutynin (Reb-Oxy) vs placebo in patients with OSA. After a baseline in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG), patients underwent PSGs after 7 nights of Reb-Oxy and 7 nights of placebo to compare apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), which was the primary outcome. Response rate was based on the percentage of subjects with a ≥ 50% reduction in AHI from baseline. Secondary outcomes included Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) score and psychomotor vigilance test (PVT) values. Home oximetry evaluated overnight oxygen desaturation index (ODI) throughout treatment.
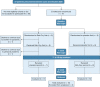
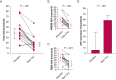
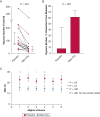
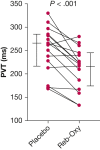
Results: Sixteen subjects aged 57 [51-61] years (median [interquartile range]) with a BMI of 30 [26-36] kg/m2 completed the study. Reb-Oxy lowered AHI from 49 [35-57] events per hour at baseline to 18 [13-21] events per hour (59% median reduction) compared with 39 [29-48] events per hour (6% median reduction) with placebo (P < .001). Response rate for Reb-Oxy was 81% vs 13% for placebo (P < .001). Although ESS scores were not significantly lowered, PVT median reaction time decreased from 250 [239-312] ms at baseline to 223 [172-244] ms on Reb-Oxy vs 264 [217-284] ms on placebo (P < .001). Home oximetry illustrated acute and sustained improvement in the oxygen desaturation index on Reb-Oxy vs placebo.
Interpretation: The administration of Reb-Oxy greatly decreased OSA severity and increased vigilance. These results highlight potential possibilities for pharmacologic treatment of OSA.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov; No.: NCT04449133; URL: www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Keywords: OSA; antimuscarinic and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors; pharmacologic treatment; upper airway; vigilance.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Peppard P.E., Young T., Palta M., Skatrud J. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(19):1378–1384. - PubMed
-
- Shahar E., Whitney C.W., Redline S., et al. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(1):19–25. - PubMed
-
- Perger E., Jutant E.M., Redolfi S. Targeting volume overload and overnight rostral fluid shift: a new perspective to treat sleep apnea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;42:160–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

