The Modified Pancreatitis Activity Scoring System Shows Distinct Trajectories in Acute Pancreatitis: An International Study
- PMID: 34543736
- PMCID: PMC9060638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.09.014
The Modified Pancreatitis Activity Scoring System Shows Distinct Trajectories in Acute Pancreatitis: An International Study
Abstract
Background & aims: The aims of this study were to: (1) assess the performance of the Pancreatitis Activity Scoring System (PASS) in a large intercontinental cohort of patients with acute pancreatitis (AP); and (2) investigate whether a modified PASS (mPASS) yields a similar predictive accuracy and produces distinct early trajectories between severity subgroups.
Methods: Data was prospectively collected through the Acute Pancreatitis Patient Registry to Examine Novel Therapies In Clinical Experience (APPRENTICE) consortium (2015-2018) involving 22 centers from 4 continents. AP severity was categorized per the revised Atlanta classification. PASS trajectories were compared between the three severity groups using the generalized estimating equations model. Four mPASS models were generated by modifying the morphine equivalent dose (MED), and their trajectories were compared.
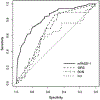
Results: A total of 1393 subjects were enrolled (median age, 49 years; 51% males). The study cohort included 950 mild (68.2%), 315 (22.6%) moderately severe, and 128 (9.2%) severe AP. Mild cases had the lowest PASS at each study time point (all P < .001). A subset of patients with outlier admission PASS values was identified. In the outlier group, 70% of the PASS variation was attributed to the MED, and 66% of these patients were from the United States centers. Among the 4 modified models, the mPASS-1 (excluding MED from PASS) demonstrated high performance in predicting severe AP with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.88 (vs area under the receiver operating characteristic of 0.83 in conventional PASS) and produced distinct trajectories with distinct slopes between severity subgroups (all P < .001).
Conclusion: We propose a modified model by removing the MED component, which is easier to calculate, predicts accurately severe AP, and maintains significantly distinct early trajectories.
Keywords: Acute Pancreatitis; Disease Activity; PASS; Severity.
Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Garg SK, Singh D, Sarvepalli S, et al. Incidence, admission rates, and economic burden of adult emergency visits for chronic pancreatitis: data from the National Emergency Department Sample, 2006 to 2012, J Clin Gastroenterol 2019; 53:e328–e333. - PubMed
-
- Vaughn VM, Shuster D, Rogers MAM, et al. Early versus delayed feeding in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 2017;166:883–892. - PubMed
-
- Vega SS, DiMagno MJ, Forsmark CE, et al. Initial medical treatment of acute pancreatitis: American Gastroenterological Association Institute Technical Review. Gastroenterology 2018; 154:1103–1139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical