Osimertinib plus platinum-pemetrexed in newly diagnosed epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: safety run-in results from the FLAURA2 study
- PMID: 34543864
- PMCID: PMC8453202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100271
Osimertinib plus platinum-pemetrexed in newly diagnosed epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: safety run-in results from the FLAURA2 study
Abstract
Background: The phase III FLAURA2 (NCT04035486) study will evaluate efficacy and safety of first-line osimertinib with platinum-pemetrexed chemotherapy versus osimertinib monotherapy in epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive (EGFRm) advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The safety run-in, reported here, assessed the safety and tolerability of osimertinib with chemotherapy prior to the randomized phase III evaluation.
Patients and methods: Patients (≥18 years; Japan: ≥20 years) with EGFRm locally advanced/metastatic NSCLC received oral osimertinib 80 mg once daily (QD), with either intravenous (IV) cisplatin 75 mg/m2 or IV carboplatin target area under the curve 5, plus pemetrexed 500 mg/m2 every 3 weeks (Q3W) for four cycles. Maintenance was osimertinib 80 mg QD with pemetrexed 500 mg/m2 Q3W until progression/discontinuation. The primary objective was to evaluate safety and tolerability of the osimertinib-chemotherapy combination.
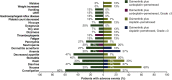
Results: Thirty patients (15 per group) received treatment [Asian, 73%; female, 63%; median age (range) 61 (45-84) years]. Adverse events (AEs) were reported by 27 patients (90%): osimertinib-carboplatin-pemetrexed, 100%; osimertinib-cisplatin-pemetrexed, 80%. Most common AEs were constipation (60%) with osimertinib-carboplatin-pemetrexed and nausea (60%) with osimertinib-cisplatin-pemetrexed. In both groups, 20% of patients reported serious AEs. No specific pattern of AEs leading to dose modifications/discontinuations was observed; one patient discontinued all study treatments including osimertinib due to pneumonitis (study-specific discontinuation criterion). Hematologic toxicities were as expected and manageable.
Conclusions: Osimertinib-chemotherapy combination had a manageable safety and tolerability profile in EGFRm advanced/metastatic NSCLC, supporting further assessment in the FLAURA2 randomized phase.
Keywords: EGFRm; chemotherapy; lung cancer; osimertinib; safety.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure DP reports honoraria and consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly & Co., Merck & Co., Novartis, Pfizer Inc., prIME Oncology, Peer CME, Roche AG, and Samsung; reports consulting fees and has received research grants (institute) from Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly & Co., Merck & Co., Pfizer Inc., Roche AG, MedImmune, Sanofi-Aventis, Taiho Pharma, and Novocure; during the conduct of the study and outside the submitted work. S-WK reports consulting fees and has received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Eli Lilly & Co., and Bristol-Myers Squibb; and reports consulting fees from Roche AG; outside the submitted work. TMK has served on advisory councils or committees for AstraZeneca, Boryung, Hanmi, Novartis, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, and Roche/Genentech; and has received a research grant from AstraZeneca-KHIDI; outside the submitted work. CKL has served on an advisory council or committee for AstraZeneca, reports honoraria, and has received research grants from AstraZeneca; outside the submitted work. NY reports lecture fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novartis, Pfizer Inc., Taiho, Eli Lilly & Co., Boehringer Ingelheim, and Bayer AG; and reports consulting fees and lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co.; outside the submitted work. RM and PH are employees of AstraZeneca. XH is an employee of AstraZeneca and reports ownership of stocks or shares. PAJ reports consulting fees from Mirati Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer Inc., Roche/Genentech, Chugai Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly & Co., Ignyta, Takeda Oncology, Novartis, Voronoi, SFJ Pharmaceuticals, Biocartis, LOXO Oncology, PUMA, Sanofi, Transcenta, Daiichi Sankyo, Silicon Therapeutics, and AbbVie Inc.; and has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly & Co., Takeda Oncology, PUMA, Astellas Pharmaceuticals, and Daiichi Sankyo; outside the submitted work. In addition, PAJ is a co-inventor on a DFCI-owned patent on EGFR mutations licensed to Lab Corp. KK reports honoraria from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim; outside the submitted work. P-HF, NK, and AP have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Reungwetwattana T., Nakagawa K., Cho B.C. CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018 JCO2018783118. - PubMed
-
- Soria J.C., Ohe Y., Vansteenkiste J. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113–125. - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam S.S., Vansteenkiste J., Planchard D. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(1):41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials