Predictors of mortality in acute pancreatitis complicated with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 34544384
- PMCID: PMC8451102
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06709-0
Predictors of mortality in acute pancreatitis complicated with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
Abstract
Background: Multidrug-resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae infections, from pancreatic infections to bloodstream infections, influence the mortality of patients with acute pancreatitis (AP) on the condition of limited antibiotic choices. The aim of this study was to investigate the predictor of mortality among AP patients complicated with MDR-K. pneumoniae infections.
Methods: Seventy-one AP patients who occurred MDR-K. pneumoniae infections from August 1st, 2016 to August 1st, 2020 were enrolled. MDR-K. pneumoniae was defined as the K. pneumoniae strain non-susceptible to at least one agent in three or more antimicrobial categories. MDR-K. pneumoniae isolates were confirmed by Vitek-2 system. Antibiotic susceptibility test was carried out using a micro broth dilution method. Clinical characteristics and drug-resistance rates were retrospectively reviewed, and the predictors of mortality were evaluated by univariate and multivariate analyses.
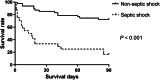
Results: The mortality rate of AP patients complicated with MDR-K. pneumoniae infections reached 46.5% (33 of 71), and pancreas (n = 53) was the most common site of MDR-K pneumoniae strains. The drug resistance rates of MDR-K. pneumoniae were high to 11 of 12 common antibiotics (more than 50.0%) except of tigecycline (23.9%). The predictor independently associated with mortality was septic shock (hazard ratio 2.959, 95% confidence intervals 1.396 - 6.272, P = 0.005).
Conclusions: More attention should be paid for pancreatic MDR-K. pneumoniae infections among AP patients The predictor for mortality of AP patients complicated with MDR-K. pneumoniae infection is septic shock. Therefore, further clinical investigations should focus on areas against septic shock.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Drug-resistance; Mortality; Multidrug-resistant infection; Predictor.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Septic Shock Due to Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii or Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing K. pneumoniae in Intensive Care Unit Patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 May 25;62(6):e02562-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02562-17. Print 2018 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29555630 Free PMC article.
-
Degradable antimicrobial polycarbonates with unexpected activity and selectivity for treating multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae lung infection in mice.Acta Biomater. 2019 Aug;94:268-280. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.057. Epub 2019 May 24. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31129359
-
Antimicrobial polymers as therapeutics for treatment of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae lung infection.Acta Biomater. 2018 Sep 15;78:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.07.038. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30031912
-
Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: challenges for treatment, prevention and infection control.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018 Oct;16(10):749-761. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2018.1522249. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018. PMID: 30207815 Review.
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae: a major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017 May 1;41(3):252-275. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux013. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28521338 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial bacteraemia on infected pancreatic necrosis patients.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1044188. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1044188. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36506015 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors for Mortality Among Critical Acute Pancreatitis Patients with Carbapenem-Resistant Organism Infections and Drug Resistance of Causative Pathogens.Infect Dis Ther. 2022 Jun;11(3):1089-1101. doi: 10.1007/s40121-022-00624-w. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Infect Dis Ther. 2022. PMID: 35377132 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Fine-Needle Aspiration in Patients With Suspected Infected Pancreatic Necrosis.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2024 Jul 1;15(7):e00726. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000726. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38870091 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of Klebsiella species from pneumonic goats, Iraq.Open Vet J. 2024 Nov;14(11):2980-2988. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i11.26. Epub 2024 Nov 30. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 39737024 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics, Drug Resistance, and Risk Factors for Death of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study from China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Aug 7;16:5039-5053. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S410397. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37576517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pando E, Alberti P, Hidalgo J, Vidal L, Dopazo C, Caralt M, Blanco L, Gómez-Gavara C, Bilbao I, Balsells J, et al. The role of extra-pancreatic infections in the prediction of severity and local complications in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2018;18(5):486–493. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2018.05.481. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical