Multiple Primary Angiosarcomas of the Colon
- PMID: 34545314
- PMCID: PMC8449722
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7237379
Multiple Primary Angiosarcomas of the Colon
Abstract
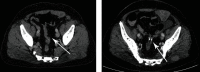
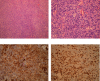
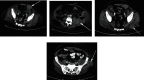
Introduction: Gastrointestinal angiosarcomas are rare and represent less than 1% of all gastrointestinal tract malignancies, with most occurring in the stomach and small intestine. Occurrence in the colorectal segments is considered extremely rare. Case Report. We describe the case of a 61-year-old male with multiple primary angiosarcomas of the colon who presented with fever and abdominal pain. The patient was initially hospitalized and treated as having an infectious disease. A multislice computed tomography (MSCT) scan revealed multiple soft tissue tumors in the region of the left iliopsoas and gluteus medius muscles. After developing hematochezia, a colonoscopy was performed which found an ulcerated tumor in the sigmoid colon. The small tissue biopsy taken during the procedure presented diagnostic difficulties and was given a preliminary diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Examination of the resected colon segment and surrounding fat tissue revealed four separate tumors. Microscopically, the tumors were composed of solid sheets of spindle and epithelioid neoplastic cells with prominent nucleoli and numerous mitotic figures and immunohistochemically positive for ERG, CD31, CD34, vimentin, and CD117, while negative for CK7, CK20, CD20, CD3, CD45, TTF-1, PAN-CK, ALK, Mpox, S-100, and DOG1, leading to the final diagnosis of multiple colonic angiosarcomas. The patient's condition declined rapidly and he passed away from multiple organ failures 60 days after initial hospitalization.
Conclusion: Both clinical and pathological diagnoses of colorectal angiosarcoma are challenging. Patients are present with nonspecific symptoms leading to mismanagement and late diagnosis. A definitive pathological diagnosis relies on immunohistochemical staining for endothelial markers. Misdiagnosis as poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma or GIST is possible in limited tissue biopsies.
Copyright © 2021 Sonja Radić et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ma J., Yan Y., He X., Yang Z. Multiple colonic epithelioid angiosarcoma: a case report and review of literature. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2018;11(9):10237–10243.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

