How does satisfaction of solar PV users enhance their trust in the power grid? - Evidence from PPAPs in rural China
- PMID: 34545317
- PMCID: PMC8443908
- DOI: 10.1186/s13705-021-00306-4
How does satisfaction of solar PV users enhance their trust in the power grid? - Evidence from PPAPs in rural China
Abstract
Background: Photovoltaic Poverty Alleviation Projects (PPAPs) have been implemented in Chinese rural areas since 2014. As a new energy policy, PPAPs have played an important role in alleviating rural poverty. However, the adoption of solar PV faces multiple barriers from the perspective of beneficiaries. Therefore, this study aims to discuss and analyze factors affecting beneficiaries' satisfaction and their trust in State Grid, promoting the adoption of solar PV.
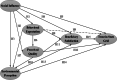
Methods: Based on the integrated American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) and Unified Theory of Acception and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model, this study used the Structural Equation Model (SEM) to reveal how the beneficiaries' satisfaction enhance their trust in State Grid. The data were obtained from a survey of 928 PPAPs' beneficiaries by stratified and random sampling in Chinese rural areas.
Results: The results confirm that environmental perception in this study has positive impact on beneficiaries' satisfaction. In addition, perceived quality also has a positive effect on beneficiaries' satisfaction and trust in State Grid; however, social influence has a negative impact on beneficiaries' satisfaction; behavior expectation can directly promote beneficiaries' satisfaction while indirectly propel their trust in State Grid.
Conclusions: This study constructs an integrated customer satisfaction model from the perspective of beneficiaries and proposes relevant measures to promote the adoption of solar PV that can be applied to poverty reduction in other developing countries worldwide.
Keywords: Adoption; Beneficiaries’ satisfaction; Photovoltaic Poverty Alleviation Projects (PPAPs); Solar PV; Trust in State Grid.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Hou J, Luo S, Cao M. A review on China's current situation and prospects of poverty alleviation with photovoltaic power generation. J Renew Sustain Energy. 2019;11(01):013503. doi: 10.1063/1.5048102. - DOI
-
- Wang Y, Zhi T (2019) Photovoltaic poverty alleviation contributes to targeted poverty alleviation energy solutions. http://www.cpnn.com.cn/zdyw/201910/t20191014_1170476.html. Accessed 27 Mar 2020
-
- NEA (2020) The State Information Office of the People's Republic of China held a press conference on the decisive battle against poverty in the energy industry. http://www.nea.gov.cn/2020-10/19/c_139451999.htm. Accessed 20 July 2020
-
- NEA (2021) Statistics of the national power industry in 2020. http://www.nea.gov.cn/2021-01/20/c_139683739.htm. Accessed 20 July 2020
-
- Hoffmann AS, de Carvalho GH, Cardoso Jr RAF. Environmental licensing challenges for the implementation of photovoltaic solar energy projects in Brazil. Energy Policy. 2019;132:1143–1154. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.07.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
