Reply to Kasugai et al.: The Mystery of Futility of Appropriate Antibiotics for Coinfection in COVID-19
- PMID: 34546857
- PMCID: PMC8865725
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202108-1846LE
Reply to Kasugai et al.: The Mystery of Futility of Appropriate Antibiotics for Coinfection in COVID-19
Figures
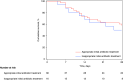
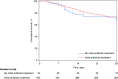
Comment on
-
The Mystery of Futility of Appropriate Antibiotics for Coinfection in COVID-19.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Dec 15;204(12):1489. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202107-1656LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34546862 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rouzé A, Martin-Loeches I, Povoa P, Metzelard M, Du Cheyron D, Lambiotte F, et al. coVAPid study group. Early bacterial identification among intubated patients with COVID-19 or influenza pneumonia: a European multicenter comparative cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2021;204:546–556. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kollef MH, Sherman G, Ward S, Fraser VJ. Inadequate antimicrobial treatment of infections: a risk factor for hospital mortality among critically ill patients. Chest . 1999;115:462–474. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Loeches I, J Schultz M, Vincent JL, Alvarez-Lerma F, Bos LD, Solé-Violán J, et al. Increased incidence of co-infection in critically ill patients with influenza. Intensive Care Med . 2017;43:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Rouzé A, Martin-Loeches I, Povoa P, Makris D, Artigas A, Bouchereau M, et al. coVAPid study Group. Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the incidence of ventilator-associated lower respiratory tract infections: a European multicenter cohort study. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47:188–198. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

