COVID associated mucormycosis: A preliminary study from a dedicated COVID Hospital in Delhi
- PMID: 34547717
- PMCID: PMC8432976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103220
COVID associated mucormycosis: A preliminary study from a dedicated COVID Hospital in Delhi
Abstract
Background: It is an incontrovertible fact that the Rhino Orbital Cerebral Mucormycosis (ROCM) upsurge is being seen in the context of COVID-19 in India. Briefly presented is evidence that in patients with uncontrolled diabetes, a dysfunctional immune system due to SARS-COV-2 and injudicious use of corticosteroids may be largely responsible for this malady.
Objective: To find the possible impact of COVID 19 infection and various co-morbidities on occurrence of ROCM and demonstrate the outcome based on medical and surgical interventions.
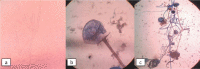
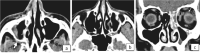
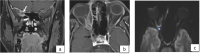
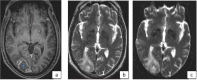
Methodology: Prospective longitudinal study included patients diagnosed with acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis after a recent COVID-19 infection. Diagnostic nasal endoscopy (DNE) was performed on each patient and swabs were taken and sent for fungal KOH staining and microscopy. Medical management included Injection Liposomal Amphotericin B, Posaconazole and Voriconazole. Surgical treatment was restricted to patients with RT PCR negative results for COVID-19. Endoscopic, open, and combined approaches were utilized to eradicate infection. Follow-up for survived patients was maintained regularly for the first postoperative month.
Results: Out of total 131 patients, 111 patients had prior history of SARS COVID 19 infection, confirmed with a positive RT-PCR report and the rest 20 patients had no such history. Steroids were received as a part of treatment in 67 patients infected with COVID 19. Among 131 patients, 124 recovered, 1 worsened and 6 died. Out of 101 known diabetics, 98 recovered and 3 had fatal outcomes. 7 patients with previous history of COVID infection did not have any evidence of Diabetes mellitus, steroid intake or any other comorbidity.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that ROCM upsurge seen in the context of COVID-19 in India was mainly seen in patients with uncontrolled diabetes, a dysfunctional immune system due to SARS-COV-2 infection and injudicious use of corticosteroids.
Keywords: Acute invasive fungal sinusitis; COVID-19; Diabetes mellitus; Mucormycosis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


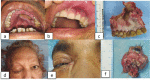
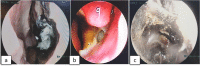
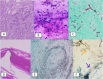
References
-
- Ismaiel W.F., Abdelazim M.H., Eldsoky I., Ibrahim A.A. 2020. Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID- 19 . The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect , the company ’ s public news and information. (January)
-
- Bond S. These organisms are. 2021. The genera in the order Mucorales cause most human infection; pp. 1–34.
-
- Skiada A., Pagano L., Groll A., Zimmerli S., Dupont B., Lagrou K., et al. Zygomycosis in Europe: analysis of 230 cases accrued by the registry of the european Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) working group on zygomycosis between 2005 and 2007. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17(12):1859–1867. - PubMed
-
- Kontoyiannis D.P., Yang H., Song J., Kelkar S.S., Yang X., Azie N. Prevalence, clinical and economic burden of mucormycosis-related hospitalizations in the United States: a retrospective study. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:1–6. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-2023-z. [Internet] Available from: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

