Elevated glycolysis imparts functional ability to CD8+ T cells in HIV infection
- PMID: 34548381
- PMCID: PMC8473722
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202101081
Elevated glycolysis imparts functional ability to CD8+ T cells in HIV infection
Abstract
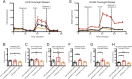
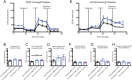
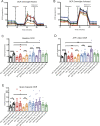
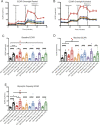
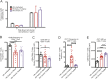
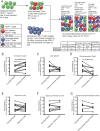
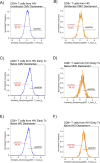
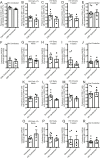
The mechanisms inducing exhaustion of HIV-specific CD8+ T cells are not fully understood. Metabolic programming directly influences T-cell differentiation, effector function, and memory. We evaluated metabolic profiles of ex vivo CD8+ T cells in HIV-infected individuals. The baseline oxygen consumption rate of CD8+ T cells was elevated in all infected individuals and CD8+ T cells were working at maximal respiratory capacity. The baseline glycolysis rate was enhanced only during early untreated HIV and in viral controllers, but glycolytic capacity was conserved at all stages of infection. CD8+ T-cell mTOR activity was found to be reduced. Enhanced glycolysis was crucial for HIV-specific killing of CD8+ T cells. CD8+ T-cell cytoplasmic GAPDH content was reduced in HIV, but less in early infection and viral controllers. Thus, CD8+ T-cell exhaustion in HIV is characterized by reduced glycolytic activity, enhanced OXPHOS demands, dysregulated mTOR, and reduced cytoplasmic GAPDH. These data provide potential metabolic strategies to reverse CD8+ T-cell dysfunction in HIV.
© 2021 Rahman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Angin M, Volant S, Passaes C, Lecuroux C, Monceaux V, Dillies MA, Valle-Casuso JC, Pancino G, Vaslin B, Le Grand R, et al. (2019) Metabolic plasticity of HIV-specific CD8+ T cells is associated with enhanced antiviral potential and natural control of HIV-1 infection. Nat Metab 1: 704–716. 10.1038/s42255-019-0081-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bantug GR, Fischer M, Grählert J, Balmer ML, Unterstab G, Develioglu L, Steiner R, Zhang L, Costa ASH, Gubser PM, et al. (2018) Mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum contact sites function as immunometabolic hubs that orchestrate the rapid recall response of memory CD8 + T cells. Immunity 48: 542–555.e6. 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.02.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bengsch B, Johnson AL, Kurachi M, Odorizzi PM, Pauken KE, Attanasio J, Stelekati E, McLane LM, Paley MA, Delgoffe GM, et al. (2016) Bioenergetic insufficiencies due to metabolic alterations regulated by the inhibitory receptor PD-1 are an early driver of CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Immunity 45: 358–373. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
