Lung Transplantation in a Patient With COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Failure
- PMID: 34548969
- PMCID: PMC8437086
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.17152
Lung Transplantation in a Patient With COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Failure
Abstract
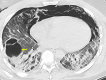
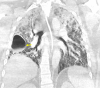
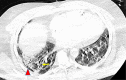
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is currently a significant cause of acute respiratory failure worldwide, leading to irreversible fibrotic lung disease. In patients with persistent respiratory failure after acute COVID-19 infection, lung transplant is an emerging option. Here, we have presented a case where the patient required venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) support for 33 days until a bilateral lung transplant was performed on day 71 after the initial COVID-19 infection. The early outcomes have been favorable. Currently, no guidelines exist for an acceptable time period after initial COVID-19 infection, duration of negative COVID polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing, or negative Vero cell culture in the setting of persistent positive COVID PCR testing before listing for a lung transplant. Due to a lack of standardized guidelines, this patient was not listed for a lung transplant until the COVID-19 PCRs came negative on days 47 and 49 after the infection.
Keywords: acute lung injury; covid-19; lung fibrosis; lung transplant; respiratory failure.
Copyright © 2021, Sajid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Lung transplantation for severe post-coronavirus disease 2019 respiratory failure. Hawkins RB, Mehaffey JH, Charles EJ, Mannem HC, Roeser M. Transplantation. 2021;105:1381–1387. - PubMed
-
- Lung transplantation for pulmonary fibrosis secondary to severe COVID-19 [PREPRINT] Bharat A, Querrey M, Markov NS, et al. medRxiv. 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
