Withanolide-Type Steroids from Physalis nicandroides Inhibit HIV Transcription
- PMID: 34549952
- PMCID: PMC8946265
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00637
Withanolide-Type Steroids from Physalis nicandroides Inhibit HIV Transcription
Abstract
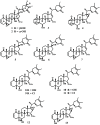
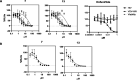
The aim of the present study is to report the isolation, structural elucidation, and antiviral evaluation of four new withanolide-type steroids, named nicansteroidins A-D (1-4), together with nine related known compounds (5-13) isolated from the aerial parts of Physalis nicandroides. Their structures were established based on an extensive spectroscopic analysis, including 1D and 2D NMR techniques. Outstandingly, nicansteroidins A and B possess an unusual side chain with an exocyclic double bond on the δ-lactone system, whereas nicansteroidins C and D have an uncommon cycloperoxide functionality in ring A as distinct structural motifs. Their biological evaluation as inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication revealed that two compounds from this series, 7 and 13, displayed strong inhibition of HIV-1 replication with IC50 values lower than 2 μM. Moreover, cellular mechanism experiments showed that the main target of these compounds in the HIV replication cycle is viral transcription. This study is the first report of withanolide-type steroids as HIV inhibitors and provides insight into their potential as candidates for further preclinical studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS6 July 2020. Key facts. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids (accessed Nov 2020).
-
- World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS. Publications on treatment and care. 2020. https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/arv/en/ (accessed Nov 2020).
-
- Standley P. C.; Calderon S.. Lista preliminar de las plantas de El Salvador; Imprenta Nacional: San Salvador, El Salvador, 1941; pp 1–274.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

