Hourly Kinetics of Critical Organ Dysfunction in Extremely Preterm Infants
- PMID: 34550843
- PMCID: PMC8865589
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202106-1359OC
Hourly Kinetics of Critical Organ Dysfunction in Extremely Preterm Infants
Abstract
Rationale: Use of severity of illness scores to classify patients for clinical care and research is common outside of the neonatal ICU. Extremely premature (<29 weeks' gestation) infants with extremely low birth weight (<1,000 g) experience significant mortality and develop severe pathology during the protracted birth hospitalization. Objectives: To measure at high resolution the changes in organ dysfunction that occur from birth to death or discharge home by gestational age and time, and among extremely preterm infants with and without clinically meaningful outcomes using the neonatal sequential organ failure assessment score. Methods: A single-center, retrospective, observational cohort study of inborn, extremely preterm infants with extremely low birth weight admitted between January 2012 and January 2020. Neonatal sequential organ failure assessment scores were calculated every hour for every patient from admission until death or discharge. Measurements and Main Results: Longitudinal, granular scores from 436 infants demonstrated early and sustained discrimination of those who died versus those who survived to discharge. The discrimination for mortality by the maximum score was excellent (area under curve, 0.91; 95% confidence intervals, 0.88-0.94). Among survivors with and without adverse outcomes, most score variation occurred at the patient level. The weekly average score over the first 28 days was associated with the sum of adverse outcomes at discharge. Conclusions: The neonatal sequential organ failure assessment score discriminates between survival and nonsurvival on the first day of life. The major contributor to score variation occurred at the patient level. There was a direct association between scores and major adverse outcomes, including death.
Keywords: critical illness; neonatal ICU; newborn; organ dysfunction score.
Figures
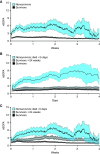

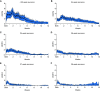

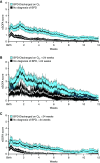

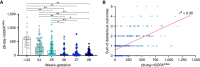
Comment in
-
The Future of Outcome Prediction for Preterm Infants in the Neonatal ICU.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Jan 1;205(1):6-8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2188ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 34710338 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Keuning BE, Kaufmann T, Wiersema R, Granholm A, Pettilä V, Møller MH, et al. HEALICS consortium Mortality prediction models in the adult critically ill: a scoping review. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand . 2020;64:424–442. - PubMed
-
- Strand K, Flaatten H. Severity scoring in the ICU: a review. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand . 2008;52:467–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

