Targeting the IGF-Axis Potentiates Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Liver Metastases by Altering the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment
- PMID: 34552012
- PMCID: PMC8677570
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0144
Targeting the IGF-Axis Potentiates Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Liver Metastases by Altering the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment
Abstract
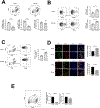
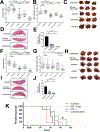
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly aggressive malignancy, resistant to chemotherapy and associated with high incidence of liver metastases and poor prognosis. Using murine models of aggressive PDAC, we show here that in mice bearing hepatic metastases, treatment with the IGF-Trap, an inhibitor of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) signaling, profoundly altered the local, immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in the liver, curtailing the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, reversing innate immune cell polarization and inhibiting metastatic expansion. Significantly, we found that immunotherapy with anti-PD-1 antibodies also reduced the growth of experimental PDAC liver metastases, and this effect was enhanced when combined with IGF-Trap treatment, resulting in further potentiation of a T-cell response. Our results show that a combinatorial immunotherapy based on dual targeting of the prometastatic immune microenvironment of the liver via IGF blockade, on one hand, and reversing T-cell exhaustion on the other, can provide a significant therapeutic benefit in the management of PDAC metastases.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010;127(12):2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65(1):5–29. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2014;74(11):2913–21. - PubMed
-
- Tempero MA, Malafa MP, Behrman SW, Benson AB 3rd, Casper ES, Chiorean EG, et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2014: featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2014;12(8):1083–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

