Effect of potassium fertilizer on the growth, physiological parameters, and water status of Brassica juncea cultivars under different irrigation regimes
- PMID: 34555032
- PMCID: PMC8459943
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257023
Effect of potassium fertilizer on the growth, physiological parameters, and water status of Brassica juncea cultivars under different irrigation regimes
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Effect of potassium fertilizer on the growth, physiological parameters, and water status of Brassica juncea cultivars under different irrigation regimes.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 16;18(11):e0294881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294881. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37972070 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
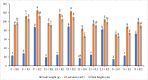
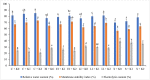
Abiotic stress, especially a lack of water, can significantly reduce crop yields. In this study, we evaluated the physiological and biochemical effects of potassium sulfate (K2SO4) fertilizer and varied irrigation regimes on the economically significant oilseed crop, Brassica juncea L, under open field conditions. Two cultivars (RH-725 and RH-749) of B. juncea were used in a randomized complete block design experiment with three replicates. Irrigation regimes consisted of a control (double irrigation: once at the 50% flowering and another at 50% fruiting stages), early irrigation (at 50% flowering only), late irrigation (at 50% fruiting only) and stress (no irrigation). The K2SO4 applications were: control (K0, no fertilization); K1, 10 kg ha-1; and K2, 20 kg ha-1. We measured growth via fresh and dry plant weight, plant height, root length, and leaf area. All the growth parameters were higher in RH-749. The physiological attributes, including the membrane stability index and relative water content, were higher at the 50% flowering stage in RH-749. The amount of antioxidant enzymes (catalase (CAT), guaiacol peroxidase (POX), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and superoxide dismutase (SOD)) was enhanced when both plants were fertilized during water stress. All of these enzymes had higher activity in RH-749. The total chlorophyll content and photosynthesis rate were considerably higher in RH-749, which leaked fewer electrolytes and maintained a less destructive osmotic potential under limited water conditions. The results indicated that it is water-stress tolerant when given a high concentration of K2SO4, which alleviated the adverse effects of water stress on growth and physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson RA, Sangha M, Banga S, Atwal A, Gupta S. Heat stress tolerance in relation to oxidative stress and antioxidants in Brassica juncea. J Environ Biol. 2014; 35(2):383. - PubMed
-
- Saini I, Yadav VK, Aggarwal A, Kaushik P. Effect of superphosphate, urea and bioinoculants on Zinnia elegans Jacq. Ind J Exp Biol.2020; 58(10):730–7.
-
- Wanasundara J, Tan S, Alashi A, Pudel F, Blanchard C. Proteins from canola/rapeseed: Current status. Sustainable protein sources: Elsevier; 2017. p. 285–304.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

