A brief performance evaluation and literature review of Abbott ID Now COVID-19 rapid molecular-based test
- PMID: 34555430
- PMCID: PMC8452348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114293
A brief performance evaluation and literature review of Abbott ID Now COVID-19 rapid molecular-based test
Abstract
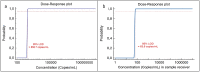
The qualitative ID Now COVID-19 assay combines claimed performance and ease of use that seem to position it as a reliable test for urgent patient management. However, the declared limit of detection (LOD) of 125 genome equivalents/mL is not confirmed by the published studies, which observed a range of LOD varying from 276 to 20.000 copies/mL. We decided to establish the LOD value on more robust basis using serial dilutions of a SARS-CoV-2 culture supernatant sample of defined concentration. Afterwards, we tested the analytical performances of the assay with 23 QCMD external quality control measurements. Hence, taking into consideration the additional dilution in the sample receiver cup, we found a lower 95 % LOD of 64 copies/mL. For its intended use and with the new established LOD, ID Now COVID-19 proved to be a suitable test for the diagnosis of COVID-19 in contagious patients, as proposed by the latest Belgian recommendations.
Keywords: COVID-19; ID Now; Molecular diagnostics; NEAR; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Anon. https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/?section=molecular-assays#diag_tab. (Accessed 3 March 2021).
-
- Anon. https://covid-19.sciensano.be/fr/procedures/rt-pcr-0. (Accessed 22 February 2021).
-
- Anon. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/real-time-rt-pcr-as.... (Accessed 16 February 2021).
-
- Basu A., Zinger T., Inglima K., et al. Performance of Abbott ID Now COVID-19 rapid nucleic acid amplification test using nasopharyngeal swabs transported in viral transport media and dry nasal swabs in a New York City Academic Institution. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58(8) doi: 10.1128/JCM.01136-20. e01136-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruno, L., Escuret, V., Résultats de l’évaluation de la performance analytique pour la détection du SARS-CoV-2 dans le cadre de l’épidémie de COVID-19 comparaison avec la technique de référence du CNR IPP. https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/covid-19-reactifs-evaluations/. (Accessed 16 February 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

