Programmed surface on poly(aryl-ether-ether-ketone) initiating immune mediation and fulfilling bone regeneration sequentially
- PMID: 34557785
- PMCID: PMC8454576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100148
Programmed surface on poly(aryl-ether-ether-ketone) initiating immune mediation and fulfilling bone regeneration sequentially
Abstract
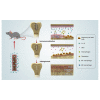
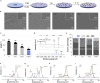
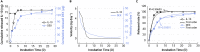
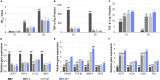
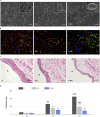
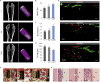
The immune responses are involved in every stage after implantation but the reported immune-regulated materials only work at the beginning without fully considering the different phases of bone healing. Here, poly(aryl-ether-ether-ketone) (PEEK) is coated with a programmed surface, which rapidly releases interleukin-10 (IL-10) in the first week and slowly delivers dexamethasone (DEX) up to 4 weeks. Owing to the synergistic effects of IL-10 and DEX, an aptly weak inflammation is triggered within the first week, followed by significant M2 polarization of macrophages and upregulation of the autophagy-related factors. The suitable immunomodulatory activities pave the way for osteogenesis and the steady release of DEX facilitates bone regeneration thereafter. The sequential immune-mediated process is also validated by an 8-week implementation on a rat model. This is the first attempt to construct implants by taking advantage of both immune-mediated modulation and sequential regulation spanning all bone regeneration phases, which provides insights into the fabrication of advanced biomaterials for tissue engineering and immunological therapeutics.
Keywords: bone regeneration; immune-mediated osteogenesis; poly(aryl-ether-ether-ketone); sequential release; surface modifications.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Schindler O.S., Cannon S.R., Briggs T.W.R., Blunn G.W. Use of a novel bone graft substitute in peri-articular bone tumours of the knee. The Knee. 2007;14:458–464. - PubMed
-
- Cook E.A., Cook J.J. Bone graft substitutes and allografts for reconstruction of the foot and ankle. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Sur. 2009;26:589–605. - PubMed
-
- Carson J.S., Bostrom M.P.G. Synthetic bone scaffolds and fracture repair. Injury-int. J. Care Inj. 2007;38:S33–S37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

