One-stop preoperative assessment of renal vessels for living donors with 3.0 T non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography: compared with computerized tomography angiography and surgical results
- PMID: 34558306
- PMCID: PMC8631022
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20210589
One-stop preoperative assessment of renal vessels for living donors with 3.0 T non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography: compared with computerized tomography angiography and surgical results
Abstract
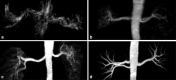
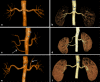
Objective: The study was to investigate the feasibility and accuracy of assessment for living renal donors before transplantation by using 3.0 T non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (NCE-MRA).
Methods: 30 renal donors were investigated and underwent computed tomography angiography (CTA) and 3.0 T NCE-MRA before nephrectomy. Two radiologists independently assessed arterial and venous anatomy and potential kidney lesions. The image quality score, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), diameters and lengths of renal arteries and veins were compared between CTA and NCE-MRA. Imaging findings were compared with the surgical results served as reference standard. Agreement was assessed using κ test. The Wilcoxon test and paired sample t test were used for statistically significant differences.
Results: The results of image quality score for renal arteries and veins were highly consistent between the two radiologists in NCE-MRA (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in the scores of renal arterial and venous branches between NCE-MRA and CTA (p > 0.05). The SNR and CNR of renal vessels were higher than CTA (p < 0.001). There were no statistically significant differences in the length of renal vessels measured by the two methods (p > 0.05), and the diameter was smaller than that of CTA (p < 0.05). The detection of normal renal arteries and early branches by both examination techniques was consistent with intraoperative findings. Both methods showed good consistency between the anatomical variation of renal vein and the intraoperative diagnosis (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: 3.0 T NCE-MRA can be used for evaluation of main renal arteries and veins with high accuracy for anatomy and variation classification, and can be used for pre-operative vascular evaluation of living donor kidney transplantation.
Advances in knowledge: 3.0 T NCE-MRA can be used for evaluation of main renal arteries and veins with high accuracy for anatomy and variation classification, and can be used for pre-operative vascular evaluation of living donor kidney transplantation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diagnostic performance of a non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging protocol for potential living related kidney donors.Acad Radiol. 2013 Apr;20(4):393-400. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.12.001. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23498978
-
Prospective study comparing three-dimensional computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating the renal vascular anatomy in potential living renal donors.BJU Int. 2005 Nov;96(7):1105-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05809.x. BJU Int. 2005. PMID: 16225537
-
Noncontrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Versus Computed Tomography Angiography in Preoperative Evaluation of Potential Living Renal Donors.Acad Radiol. 2015 Nov;22(11):1368-75. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Acad Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26307028
-
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography: evaluation of renal arteries in living renal transplant donors.Eur J Radiol. 2004 Oct;52(1):84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2003.08.002. Eur J Radiol. 2004. PMID: 15380851 Review.
-
Magnetic Resonance Angiography of the Arteries of the Upper and Lower Extremities.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2023 Aug;31(3):361-372. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2023.04.002. Epub 2023 May 22. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2023. PMID: 37414466 Review.
Cited by
-
The accessory renal arteries: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Clin Anat. 2025 Sep;38(6):660-672. doi: 10.1002/ca.24255. Epub 2024 Dec 8. Clin Anat. 2025. PMID: 39648312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiologic evaluation of the kidney transplant donor and recipient.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jan;50(1):272-289. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04477-4. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 38985292 Review.
-
Successful living donor kidney transplantation following ex vivo repair of renal artery aneurysm.Urol Case Rep. 2025 May 19;61:103076. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2025.103076. eCollection 2025 Jul. Urol Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40496179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia-Covarrubias L, Prieto-Olivares P, Bahena-Portillo A, Cicero-Lebrija A, Hinojosa-Heredia H, Fernández-Lopez LJ, et al. . Experience and security of the Hand-Assisted laparoscopic nephrectomy of a living donor in a public health center. Transplant Proc 2018; 50: 433–5. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2017.12.040 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gulati M, Dermendjian H, Gómez AM, Tan N, Margolis DJ, Lu DS, et al. . 3.0Tesla magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for comprehensive renal evaluation of living renal donors: pilot study with computerized tomography angiography (cta) comparison. Clin Imaging 2016; 40: 370–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2016.01.010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

