Lrp1 is a host entry factor for Rift Valley fever virus
- PMID: 34559985
- PMCID: PMC8786218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.001
Lrp1 is a host entry factor for Rift Valley fever virus
Abstract
Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV) is a zoonotic pathogen with pandemic potential. RVFV entry is mediated by the viral glycoprotein (Gn), but host entry factors remain poorly defined. Our genome-wide CRISPR screen identified low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (mouse Lrp1/human LRP1), heat shock protein (Grp94), and receptor-associated protein (RAP) as critical host factors for RVFV infection. RVFV Gn directly binds to specific Lrp1 clusters and is glycosylation independent. Exogenous addition of murine RAP domain 3 (mRAPD3) and anti-Lrp1 antibodies neutralizes RVFV infection in taxonomically diverse cell lines. Mice treated with mRAPD3 and infected with pathogenic RVFV are protected from disease and death. A mutant mRAPD3 that binds Lrp1 weakly failed to protect from RVFV infection. Together, these data support Lrp1 as a host entry factor for RVFV infection and define a new target to limit RVFV infections.
Keywords: CRISPR screen; Lrp1; Rift Valley fever virus; viral entry.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.W.V. is a founder of Casma Therapeutics and pierianDx and is employed by Vir Biotechnology. None of these companies funded the work reported here. Invention disclosures for method of use for Lrp1 interaction with RVFV Gn (G.K.A., A.L.H., D.W.L., H.W.V., and S.S.G.) and for the use of anti-Lrp1 antibodies by U Toronto (S.S.S., S.M., and G.K.A.) have been filed. Inclusion and diversity We worked to ensure sex balance in the selection of non-human subjects. We worked to ensure diversity in experimental samples through the selection of the cell lines. One or more of the authors of this paper self-identifies as an underrepresented ethnic minority in science. One or more of the authors of this paper self-identifies as a member of the LGBTQ+ community. While citing references scientifically relevant for this work, we also actively worked to promote gender balance in our reference list.
Figures

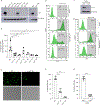




Comment in
-
Closing the Rift: Discovery of a novel virus receptor.Cell. 2021 Sep 30;184(20):5084-5086. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.004. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34559984
References
-
- BLASI E, RADZIOCH D, DURUM SK & VARESIO L 1987. A murine macrophage cell line, immortalized by v-raf and v-myc oncogenes, exhibits normal macrophage functions. Eur J Immunol, 17, 1491–8. - PubMed
-
- BRUSTOLIN M, TALAVERA S, NUNEZ A, SANTAMARIA C, RIVAS R, PUJOL N, VALLE M, VERDUN M, BRUN A, PAGES N & BUSQUETS N 2017. Rift Valley fever virus and European mosquitoes: vector competence of Culex pipiens and Stegomyia albopicta (= Aedes albopictus). Med Vet Entomol, 31, 365–372. - PubMed
-
- BU G 2001. The roles of receptor-associated protein (RAP) as a molecular chaperone for members of the LDL receptor family. Int Rev Cytol, 209, 79–116. - PubMed
-
- BU G & SCHWARTZ AL 1998. RAP, a novel type of ER chaperone. Trends Cell Biol, 8, 272–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI060525/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI106688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103422/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS101100/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI059371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI144033/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123926/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI120943/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 GM136766/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130152/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI161765/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI107056/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150792/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI163603/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI142784/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

