Cerebrospinal fluid levels of the neurotrophic factor neuroleukin are increased in early Alzheimer's disease, but not in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- PMID: 34560885
- PMCID: PMC8464117
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-021-00899-0
Cerebrospinal fluid levels of the neurotrophic factor neuroleukin are increased in early Alzheimer's disease, but not in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Cerebrospinal fluid levels of the neurotrophic factor neuroleukin are increased in early Alzheimer's disease, but not in cerebral amyloid angiopathy.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Nov 16;13(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00929-x. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34784952 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
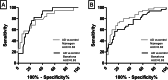
Background: Neuroleukin (NLK) is a protein with neurotrophic properties and is present in a proportion of senile plaques and amyloid laden vessels. It has been suggested that NLK is part of a neuroprotective response to amyloid β-induced cell death. The aim of our study was to investigate the value of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) NLK levels as a biomarker of vascular amyloid deposition in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) and Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: CSF NLK levels were quantified by ELISA in CAA patients (n = 25) and controls (n = 27) and in two independent samples of aMCI patients, AD patients, and controls: (1) From the Radboud University Medical Center (Nijmegen), we included n = 19 aMCI patients, n = 40 AD patients, and n = 32 controls. (2) From the Hospital of Sant Pau (Barcelona), we included n = 33 aMCI patients, n = 17 AD patients, and n = 50 controls.
Results: CSF NLK levels were similar in CAA patients and controls (p = 0.95). However, we found an elevated CSF concentration of NLK in aMCI (p < 0.0001) and AD patients (p < 0.0001) compared to controls in both samples sets. In addition, we found a correlation of CSF NLK with CSF YKL-40 (age-adjusted-spearman-rank-coefficient = 0.82, p < 0.0001) in aMCI/AD patients, a well-known glial marker of neuro-inflammation.
Conclusions: We found that CSF NLK levels are elevated in aMCI and AD patients compared to controls, but are not increased in CAA patients. CSF NLK levels may be related to an increased neuroinflammatory state in early stages of AD, given its association with YKL-40.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid; Biomarkers; Cerebral amyloid angiopathy; Cerebrospinal fluid; Neuro-inflammation; Neuroleukin.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
E. Stoops is a full-time paid employee and shareholder of ADx NeuroSciences. All other authors report no declaration of interest.
Figures


References
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR, Jr, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

