The Role of Childhood Asthma in Obesity Development: A Nationwide US Multicohort Study
- PMID: 34561347
- PMCID: PMC8633057
- DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000001421
The Role of Childhood Asthma in Obesity Development: A Nationwide US Multicohort Study
Abstract
Rationale: Asthma and obesity often co-occur. It has been hypothesized that asthma may contribute to childhood obesity onset.
Objectives: To determine if childhood asthma is associated with incident obesity and examine the role of asthma medication in this association.
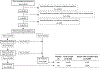
Methods: We studied 8,716 children between ages 6 and 18.5 years who were nonobese at study entry participating in 18 US cohorts of the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes program (among 7,299 children with complete covariate data mean [SD] study entry age = 7.2 [1.6] years and follow up = 5.3 [3.1] years).
Measurements and main results: We defined asthma based on caregiver report of provider diagnosis. Incident obesity was defined as the first documented body mass index ≥95th percentile for age and sex following asthma status ascertainment. Over the study period, 26% of children had an asthma diagnosis and 11% developed obesity. Cox proportional hazards models with sex-specific baseline hazards were fitted to assess the association of asthma diagnosis with obesity incidence. Children with asthma had a 23% (95% confidence intervals [CI] = 4, 44) higher risk for subsequently developing obesity compared with those without asthma. A novel mediation analysis was also conducted to decompose the total asthma effect on obesity into pathways mediated and not mediated by asthma medication use. Use of asthma medication attenuated the total estimated effect of asthma on obesity by 64% (excess hazard ratios = 0.64; 95% CI = -1.05, -0.23).
Conclusions: This nationwide study supports the hypothesis that childhood asthma is associated with later risk of obesity. Asthma medication may reduce this association and merits further investigation as a potential strategy for obesity prevention among children with asthma.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
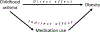

References
-
- Lang JE, Bunnell HT, Hossain MJ, et al. Being Overweight or Obese and the Development of Asthma. Pediatrics. 2018;142(6). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U2C ES026555/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U2C OD023375/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076648/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023271/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023348/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MD015705/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023287/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR014800/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023382/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD042608/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023289/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES029944/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007048/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA020585/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R34 HL142995/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 ES026071/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023249/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023389/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023290/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES029681/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023320/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023275/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES001247/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023318/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002538/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015359/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023286/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL141589/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023271/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES030691/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023281/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023248/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES028903/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI114271/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES023513/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES023515/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK120807/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023305/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023365/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023253/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023282/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 ES026086/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023347/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD045935/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023347/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES030364/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES022832/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023251/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023279/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109977/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD072267/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048522/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023288/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023286/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023289/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023253/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090264/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105447/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 ES029490/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023320/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023349/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023365/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023268/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108808/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 OD023337/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES025124/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023249/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 OD023290/OD/NIH HHS/United States

