A practical guide to large-scale docking
- PMID: 34561691
- PMCID: PMC8522653
- DOI: 10.1038/s41596-021-00597-z
A practical guide to large-scale docking
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: A practical guide to large-scale docking.Nat Protoc. 2022 Jan;17(1):177. doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00650-x. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 34887579 No abstract available.
Abstract
Structure-based docking screens of large compound libraries have become common in early drug and probe discovery. As computer efficiency has improved and compound libraries have grown, the ability to screen hundreds of millions, and even billions, of compounds has become feasible for modest-sized computer clusters. This allows the rapid and cost-effective exploration and categorization of vast chemical space into a subset enriched with potential hits for a given target. To accomplish this goal at speed, approximations are used that result in undersampling of possible configurations and inaccurate predictions of absolute binding energies. Accordingly, it is important to establish controls, as are common in other fields, to enhance the likelihood of success in spite of these challenges. Here we outline best practices and control docking calculations that help evaluate docking parameters for a given target prior to undertaking a large-scale prospective screen, with exemplification in one particular target, the melatonin receptor, where following this procedure led to direct docking hits with activities in the subnanomolar range. Additional controls are suggested to ensure specific activity for experimentally validated hit compounds. These guidelines should be useful regardless of the docking software used. Docking software described in the outlined protocol (DOCK3.7) is made freely available for academic research to explore new hits for a range of targets.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
B.K.S. and J.J.I. are founders of Blue Dolphin Lead Discovery LLC, which undertakes fee-for-service ligand discovery.
Figures

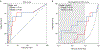


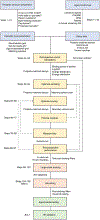

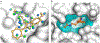


References
-
- Mayr LM & Bojanic D Novel trends in high-throughput screening. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol 9, 580–588 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Keserü GM & Makara GM The influence of lead discovery strategies on the properties of drug candidates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 8, 203–212 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Bohacek RS, McMartin C & Guida WC The art and practice of structure-based drug design: a molecular modeling perspective. Med. Res. Rev 16, 3–50 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

