Multisite evaluation of institutional processes and implementation determinants for pharmacogenetic testing to guide antidepressant therapy
- PMID: 34562070
- PMCID: PMC8841452
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13154
Multisite evaluation of institutional processes and implementation determinants for pharmacogenetic testing to guide antidepressant therapy
Abstract
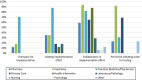
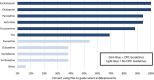
There is growing interest in utilizing pharmacogenetic (PGx) testing to guide antidepressant use, but there is lack of clarity on how to implement testing into clinical practice. We administered two surveys at 17 sites that had implemented or were in the process of implementing PGx testing for antidepressants. Survey 1 collected data on the process and logistics of testing. Survey 2 asked sites to rank the importance of Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) constructs using best-worst scaling choice experiments. Of the 17 sites, 13 had implemented testing and four were in the planning stage. Thirteen offered testing in the outpatient setting, and nine in both outpatient/inpatient settings. PGx tests were mainly ordered by psychiatry (92%) and primary care (69%) providers. CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 were the most commonly tested genes. The justification for antidepressants selected for PGx guidance was based on Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines (94%) and US Food and Drug Administration (FDA; 75.6%) guidance. Both institutional (53%) and commercial laboratories (53%) were used for testing. Sites varied on the methods for returning results to providers and patients. Sites were consistent in ranking CFIR constructs and identified patient needs/resources, leadership engagement, intervention knowledge/beliefs, evidence strength and quality, and the identification of champions as most important for implementation. Sites deployed similar implementation strategies and measured similar outcomes. The process of implementing PGx testing to guide antidepressant therapy varied across sites, but key drivers for successful implementation were similar and may help guide other institutions interested in providing PGx-guided pharmacotherapy for antidepressant management.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M.S. has institution‐associated research funding from Kailos Genetics. P.E.E. performs consulting at Cipherome. S.M.S. has a consulting/advisory or non‐promotional speaking role from Exact Sciences (Genomic Health), Genentech/Roche, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Natura, and Silverback Therapeutics, IDMC from AstraZeneca, support for third party writing assistance from Genentech/Roche, and institution‐associated research funding from Genentech and Kailos Genetics. L.B.R. receives research funding from BTG, Intl. All other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures


References
-
- Brody DJ, Gu Q. Antidepressant use among adults: United States, 2015–2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020;377:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Ornstein SM, Nietert PJ, Jenkins RG, Litvin CB. The prevalence of chronic diseases and multimorbidity in primary care practice: a PPRNet report. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:518‐524. - PubMed
-
- Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, et al. Acute and longer‐term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905‐1917. - PubMed
-
- Tansey KE, Guipponi M, Hu X, et al. Contribution of common genetic variants to antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:679‐682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HG007269/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL133373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010232/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007269/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010232/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002492/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL143161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NIH IGNITE Network
- UL1 TR001857/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HS026379/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- U01 HG010245/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007775/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010245/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

