Biochemical Assays to Directly Assess Smoothened Activation by a Conformationally Sensitive Nanobody
- PMID: 34562250
- PMCID: PMC9618365
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1701-4_13
Biochemical Assays to Directly Assess Smoothened Activation by a Conformationally Sensitive Nanobody
Abstract
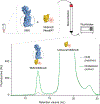
The Hedgehog signaling pathway coordinates early development and is important in various cancers. Classic approaches to test pathway activation rely on transcriptional readouts or ciliary accumulation of specific pathway components. Although these assays have laid the foundation for studying Hedgehog pathway activation, they integrate the complex molecular actions of the transporter Patched and the seven transmembrane protein Smoothened. Though it is clear that cellular sterols are critical for pathway activity, direct dissection of which sterols drive Smoothened activity is precluded by the complex biosynthetic pathways responsible for cellular sterols. Here we describe a direct method of measuring Smoothened activity in vitro. This assay measures the binding of Smoothened to NbSmo8, a single-domain antibody that is selective for the active-state of Smoothened. Binding of purified Smoothened, reconstituted with specific sterols, to fluorescently labeled NbSmo8 can be rapidly evaluated using a fluorescence-detection size-exclusion chromatography assay. This approach enables a reductionist approach to precisely interrogate the regulatory activities of cellular lipids and sterols during Hedgehog signaling.
Keywords: Fluorescence size-exclusion chromatography; Hedgehog signaling; Nanobody; NbSmo8; Smoothened activation.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

