Infections, hospitalisations, and deaths averted via a nationwide vaccination campaign using the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in Israel: a retrospective surveillance study
- PMID: 34562375
- PMCID: PMC8457761
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00566-1
Infections, hospitalisations, and deaths averted via a nationwide vaccination campaign using the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in Israel: a retrospective surveillance study
Abstract
Background: On Dec 20, 2020, Israel initiated a nationwide COVID-19 vaccination campaign for people aged 16 years and older and exclusively used the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (tozinameran). We provide estimates of the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19-related admissions to hospital (ie, hospitalisations) and deaths averted by the nationwide vaccination campaign.
Methods: In this retrospective surveillance study, we used national surveillance data routinely collected by the Israeli Ministry of Health from the first 112 days (Dec 20, 2020, up to our data cutoff of April 10, 2021) of Israel's vaccination campaign to estimate the averted burden of four outcomes: SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19-related hospitalisations, severe or critical hospitalisations, and deaths. As part of the campaign, all individuals aged 16 years and older were eligible for inoculation with the BNT162b2 vaccine in a two-dose schedule 21 days apart. We estimated the direct effects of the immunisation programme for all susceptible individuals (ie, with no previous evidence of laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection) who were at least partly vaccinated (at least one dose and at least 14 days of follow-up after the first dose). We estimated the number of SARS-CoV-2 infection-related outcomes averted on the basis of cumulative daily, age-specific rate differences, comparing rates among unvaccinated individuals with those of at least partly vaccinated individuals for each of the four outcomes and the (age-specific) size of the susceptible population and proportion that was at least partly vaccinated.
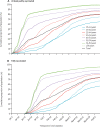
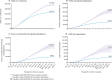
Findings: We estimated that Israel's vaccination campaign averted 158 665 (95% CI 144 640-172 690) SARS-CoV-2 infections, 24 597 (18 942-30 252) hospitalisations, 17 432 (12 770-22 094) severe or critical hospitalisations, and 5532 (3085-7982) deaths. 16 213 (65·9%) of 24 597 hospitalisations and 5035 (91·0%) of 5532 of deaths averted were estimated to be among those aged 65 years and older. We estimated 116 000 (73·1%) SARS-CoV-2 infections, 19 467 (79·1%) COVID-19-related hospitalisations, and 4351 (79%) deaths averted were accounted for by the fully vaccinated population.
Interpretation: Without the national vaccination campaign, Israel probably would have had triple the number of hospitalisations and deaths compared with what actually occurred during its largest wave of the pandemic to date, and the health-care system might have become overwhelmed. Indirect effects and long-term benefits of the programme, which could be substantial, were not included in these estimates and warrant future research.
Funding: Israel Ministry of Health and Pfizer.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests JMM, FJA, FK, GM, KP, JS, DLS, and LJ hold stock and stock options in Pfizer. ML has provided advice on COVID-19 free of charge to Janssen, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, COVAXX (United Biomedical), and to the non-profit organisation One Day Sooner; has received consulting income or honoraria from Merck, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Sanofi, and Morris-Singer Fund; and had received institutional research support from Pfizer. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Rapid COVID-19 vaccine rollout: immense success but challenges ahead.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Mar;22(3):302-304. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00616-2. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34562376 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Israel Ministry of Health Ombudsman for Medical Professions Communication no. 478057420: Summary document on the prioritization of vaccines against corona according to the recommendations of the Committee for Corona Vaccines. Dec 16, 2020. https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/reports/covid_vaccine_priorities_161220/he... (in Hebrew).
-
- Israel Ministry of Health COVID-19 reservoir. https://data.gov.il/dataset/covid-19 (in Hebrew).
-
- Haas EJ, Angulo FJ, McLaughlin JM, et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: an observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet. 2021;397:1819–1829. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rossman H, Shilo S, Meir T, Gorfine M, Shalit U, Segal E. COVID-19 dynamics after a national immunization program in Israel. Nat Med. 2021;27:1055–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

