Effects of Plasma-Lyte.½ and 0.9% saline in renal function after deceased-donor kidney transplant: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 34563559
- PMCID: PMC9659989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjane.2021.08.015
Effects of Plasma-Lyte.½ and 0.9% saline in renal function after deceased-donor kidney transplant: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The influence of different crystalloid solutions infused during deceased-donor kidney transplant on the incidence of delayed graft function remains unclear. We investigated the influence of Plasma-Lyte.½ vs. 0.9% saline on the incidence of delayed graft function in deceased-donor kidney transplant recipients.
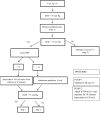
Methods: We conducted a single-blind randomized controlled trial of 104 patients aged 18 to 65 years who underwent deceased-donor kidney transplant under general anesthesia. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either Plasma-Lyte.½ (n.ß=.ß52) or 0.9% saline (n.ß=.ß52), at the same infusion volume, for intraoperative fluid replacement. The primary outcome was the occurrence of delayed graft function. Secondary outcomes included metabolic and electrolytic changes at the end of surgery.
Results: Two patients in the Plasma-Lyte.½ group and one in the 0.9% saline group died postoperatively and were not included for analysis. The incidence of delayed graft function in Plasma-Lyte.½ and 0.9% saline groups were 60.0% (95% Confidence Interval [95% CI 46.2...72.4]) and 74.5% (95% CI 61.1...84.4), respectively (p.ß=.ß0.140). Mean (standard deviation) values of immediate postoperative pH and serum chloride levels in Plasma-Lyte.½ and 0.9% saline groups were 7.306 (0.071) and 7.273 (0.061) (p.ß=.ß0.013), and 99.6 (4.2) mEq.L-1 and 103.3 (5.6) mEq.L-1, respectively (p.ß<.ß0.001). All other postoperative metabolic and electrolyte variables were not statistically different at the immediate postoperative period (p.ß>.ß0.05).
Conclusion: In deceased-donor kidney transplant recipients, the incidence of delayed graft function is not influenced by Plasma-Lyte.½ or 0.9% saline used for intraoperative fluid replacement.
Keywords: Acid-base equilibrium; Anesthesia; Crystalloid solutions; Delayed graft function; Electrolytes; Kidney transplantation.
Copyright © 2021 Sociedade Brasileira de Anestesiologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Schnuelle P., Lorenz D., Trede M., Van Der Woude F.J. Impact of renal cadaveric transplantation on survival in end-stage renal failure: evidence for reduced mortality risk compared with hemodialysis during long-term follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:2135–2141. - PubMed
-
- Port F.K., Wolfe R.A., Mauger E.A., Berling D.P., Jiang K. Comparison of survival probabilities for dialysis patient...s vs cadaveric renal transplant recipients. JAMA. 1993;270:1339–1343. - PubMed
-
- Dew M.A., Switzer G.E., Goycoolea J.M., et al. Does transplantation produce quality of life benefits? A quantitative analysis of the literature. Transplantation. 1997;64:1261–1273. - PubMed
-
- Hart A., Smith J.M., Skeans M.A., et al. OPTN/SRTR 2018 Annual data report: kidney. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(suppl 1):20–130. - PubMed
-
- Organ Transplantation in Brazil (2012 - 2019). Associa...·o Brasileira de Transplante de ..rg.·os (ABTO). Brazilian Transplantation Registry. XXV(4):1-26. https://site.abto.org.br/publicacao/rbt-ingles-2019/ [accessed 23 March 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

