Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview
- PMID: 34564369
- PMCID: PMC8472820
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics9090218
Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview
Abstract
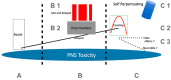
Introduction to a collection. This article is intended to introduce a collection of papers on toxic neuropathies. Toxic neuropathies can be caused by a variety of substances and by different mechanisms. Toxic agents are numerous and can be distinguished between drugs, recreational agents, heavy metals, industrial agents, pesticides, warfare agents, biologic substances and venoms. Toxic agents reach the nervous system by ingestion, transcutaneously, via the mucous membranes, parenterally and by aerosols. The most frequent types are cumulative toxicities. Other types are acute or delayed toxicities. Pathogenetic mechanisms range from a specific toxic substance profile causing axonal or demyelinating lesions, towards ion channel interferences, immune-mediated mechanisms and a number of different molecular pathways. In addition, demyelination, focal lesions and small fiber damage may occur. Clinically, neurotoxicity presents most frequently as axonal symmetric neuropathies. In this work, we present a panoramic view of toxic neuropathy, in terms of symptoms, causes, mechanisms and classification.
Keywords: dorsal root ganglia; pathogenetic mechanisms; peripheral nerve; peripheral neuropathy; toxic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Moretti M., Bonfiglioli R., Feretti D., Pavanello S., Mussi F., Grollino M.G., Villarini M., Barbieri A., Ceretti E., Carrieri M., et al. A study protocol for the evaluation of occupational mutagenic/carcinogenic risks in subjects exposed to antineoplastic drugs: A multicentric project. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:195. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

