Bioactive Agent-Loaded Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Accelerating Healing Process: A Review
- PMID: 34564519
- PMCID: PMC8469443
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11090702
Bioactive Agent-Loaded Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Accelerating Healing Process: A Review
Abstract
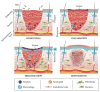
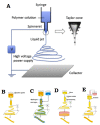
Despite the advances that have been achieved in developing wound dressings to date, wound healing still remains a challenge in the healthcare system. None of the wound dressings currently used clinically can mimic all the properties of normal and healthy skin. Electrospinning has gained remarkable attention in wound healing applications because of its excellent ability to form nanostructures similar to natural extracellular matrix (ECM). Electrospun dressing accelerates the wound healing process by transferring drugs or active agents to the wound site sooner. This review provides a concise overview of the recent developments in bioactive electrospun dressings, which are effective in treating acute and chronic wounds and can successfully heal the wound. We also discuss bioactive agents used to incorporate electrospun wound dressings to improve their therapeutic potential in wound healing. In addition, here we present commercial dressings loaded with bioactive agents with a comparison between their features and capabilities. Furthermore, we discuss challenges and promises and offer suggestions for future research on bioactive agent-loaded nanofiber membranes to guide future researchers in designing more effective dressing for wound healing and skin regeneration.
Keywords: bioactive molecules; electrospinning; tissue engineering; wound dressing; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Figures


References
-
- Mousavi S., Zarei M., Hashemi S., Ramakrishna S., Chiang W.-H., Lai C., Gholami A., Omidifar N., Shokripour M. Asymmetric Membranes: A Potential Scaffold for Wound Healing Applications. Symmetry. 2020;12:1100. doi: 10.3390/sym12071100. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

