Venom Immunotherapy: From Proteins to Product to Patient Protection
- PMID: 34564620
- PMCID: PMC8470233
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13090616
Venom Immunotherapy: From Proteins to Product to Patient Protection
Abstract
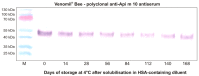
In this review, we outline and reflect on the important differences between allergen-specific immunotherapy for inhalant allergies (i.e., aeroallergens) and venom-specific immunotherapy (VIT), with a special focus on Venomil® Bee and Wasp. Venomil® is provided as a freeze-dried extract and a diluent to prepare a solution for injection for the treatment of patients with IgE-mediated allergies to bee and/or wasp venom and for evaluating the degree of sensitivity in a skin test. While the materials that make up the product have not changed, the suppliers of raw materials have changed over the years. Here, we consolidate relevant historical safety and efficacy studies that used products from shared manufacture supply profiles, i.e., products from Bayer or Hollister-Stier. We also consider the characterization and standardization of venom marker allergens, providing insights into manufacturing controls that have produced stable and consistent quality profiles over many years. Quality differences between products and their impacts on treatment outcomes have been a current topic of discussion and further research. Finally, we review the considerations surrounding the choice of depot adjuvant most suitable to augmenting VIT.
Keywords: Hymenoptera; VIT; adjuvant; allergy; honeybee venom; sensitization; venom; wasp venom.
Conflict of interest statement
Feindor, M., Heath, M.D., Carreno Velazquez, T.L., Hewings, S.J., Skinner, M.A. and Kramer M.F. are employed by Allergy Therapeutics Ltd. ATL develop and market immunotherapy products and diagnostics. Blank, S. reports non-financial support from ALK-Abelló, grants and personal fees from Bencard Allergie GmbH, grants and personal fees from Thermo Fisher Scientific, grants from Allergy Therapeutics, grants from LETI Pharma, outside the submitted work. Grosch, J. reports no conflict of interest. Golden D.B.K. has received consultant fees from Allergy Therapeutics, ALK-Abelló, Starllegens, Aquestive and Genentech; and royalties from UpToDate. Schmid-Grendelmeier P has received honoraria for AdBoards and/or speaker fees from Allergy Therapeutics, ALK-Abello, Bühlmann Diagnostics and Thermo Fisher. L. Klimek reports grants and personal fees from Allergopharma, grants and personal fees from MEDA/Mylan, personal fees from HAL Allergie, grants from ALK-Abelló, grants and personal fees from LETI Pharma, grants from Stallergenes, grants from Quintiles, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, grants from ASIT biotech, grants from Lofarma, personal fees from Allergy Therapeutic., grants from AstraZeneca, grants from GSK, grants from Inmunotek, personal fees from Cassella med, outside the submitted work. T. Jakob reports research support by ALK-Abelló, Allergy Therapeutics, Allergopharma, Cosmetics Europe, Novartis, Thermo Fisher Scientific, consulting fees by ALK-Abelló, Allergy Therapeutics, Allergopharma, Leti, Novartis, Thermo Fisher Scientific and speakers honoraria by ALK-Abelló, Allergy Therapeutics, Allergopharma, Leti, Novartis and Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Figures

References
-
- Blank S., Pehlivanli S., Methe H., Schmidt-Weber C.B., Biedermann T., Horny H.P., Kristensen T., Amar Y., Köberle M., Brockow K., et al. Fatal anaphylaxis following a hornet sting in a yellow jacket venom-sensitized patient with undetected monoclonal mast cell activation syndrome and without previous history of a systemic sting reaction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020;8:401–403.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2019.06.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Koschel D. Impaired quality of life in patients with insect venom allergy. Allergo J. Int. 2017;26:88–92. doi: 10.1007/s40629-017-0017-z. - DOI
-
- Manmohan M., Müller S., Myriam Rauber M., Koberne F., Reisch H., Koster J., Böhm R., Messelken M., Fischer M., Jakob T. Current state of follow-up care for patients with Hymenoptera venom anaphylaxis in southwest Germany: Major impact of early information. Allergo J. Int. 2018;27:4–14. doi: 10.1007/s40629-017-0046-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antolín-Amérigo D., Ruiz-León B., Vega-Castro A., de la Hoz Caballer B. Natural history of systemic reactions and risk factors in children and adults with Hymenoptera venom allergy. Allergo J. 2020;29:26–33. doi: 10.1007/s15007-020-0745-0. - DOI
-
- Blank S., Haemmerle S., Jaeger T., Russkamp D., Ring J., Schmidt-Weber C.B., Ollert M. Prevalence of Hymenoptera venom allergy and sensitization in the population-representative German KORA cohort. Allergo J. Int. 2019;28:183–191. doi: 10.1007/s40629-018-0089-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

